Nootropics are substances that enhance cognitive function, memory, creativity, and motivation in healthy individuals.
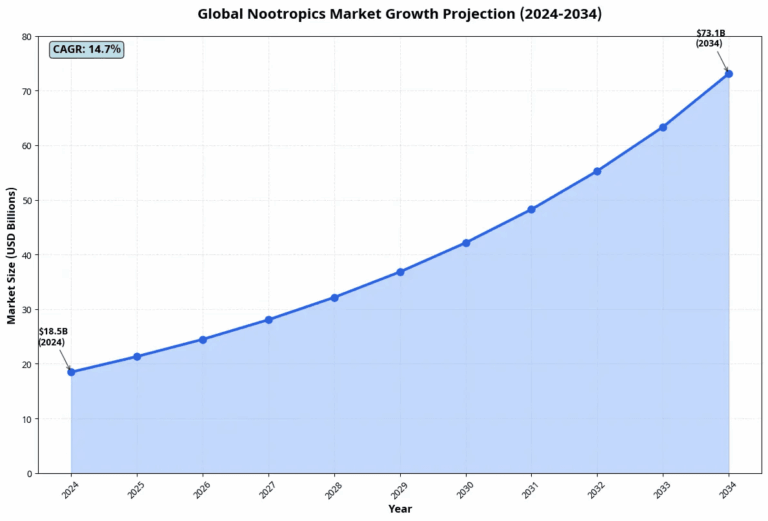
Also known as smart drugs or cognitive enhancers, these compounds have exploded into a $18.48 billion global market in 2024, projected to reach $73.11 billion by 2034 with a remarkable 14.74% annual growth rate according to recent market research.
From Silicon Valley executives to college students, millions are turning to nootropics to gain a mental edge in our increasingly competitive world.
However, with over 650 unique products flooding the market and limited FDA oversight, understanding what works, what’s safe, and how to use these substances responsibly has never been more critical.
This comprehensive guide examines the science behind nootropics, analyzes their proven benefits and potential risks, and provides evidence-based recommendations for safe usage.
Whether you’re considering your first cognitive enhancer or looking to optimize your current regimen, you’ll discover everything needed to make informed decisions about these powerful brain-boosting compounds.
In This Article
What Are Nootropics? Definition and Overview
The term “nootropic” was coined in 1972 by Romanian psychologist Cornelius E. Giurgea, combining the Greek words nöos (thinking) and tropein (to guide).
Giurgea defined nootropics as substances that enhance learning and memory while being relatively safe with few side effects.
“A nootropic drug is a substance that enhances learning and memory and facilitates learning under conditions which tend to disrupt it, while being devoid of the usual pharmacological effects of psychotropic drugs.”— Cornelius E. Giurgea, 1972
Modern Definition of Nootropics
Today’s definition has expanded beyond Giurgea’s original criteria to include any natural or synthetic substance that may positively impact mental skills.
Modern nootropics encompass three main categories:
- Dietary supplements – Natural compounds like herbs, amino acids, and vitamins
- Synthetic compounds – Laboratory-created molecules like racetams
- Prescription medications – FDA-approved drugs for cognitive conditions
Market Growth and Popularity
The nootropics market has experienced explosive growth, driven by increasing awareness of cognitive health and competitive pressures in modern society. Key statistics include:
- Global market size: $18.48 billion in 2024
- Projected growth: $73.11 billion by 2034
- Annual growth rate: 14.74% CAGR
- US market share: 43% of global market
- Primary users: Students, professionals, and aging adults
How Do Nootropics Work? Mechanisms of Action
Unlike stimulants that directly release neurotransmitters, nootropics work through more subtle mechanisms to enhance brain function.
Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why nootropics typically require consistent use over time to achieve optimal benefits.
Primary Mechanisms of Action
Neurotransmitter Modulation
Enhance production, release, or sensitivity of key brain chemicals like acetylcholine, dopamine, and GABA.
Cerebral Blood Flow
Improve oxygen and glucose delivery to brain tissue through vasodilation and enhanced circulation.
Neuroprotection
Protect neurons from oxidative stress, inflammation, and age-related damage.
Neuroplasticity
Promote growth of new neural connections and enhance synaptic plasticity.
Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration
For any nootropic to be effective, it must cross the blood-brain barrier – a selective barrier that protects the brain from potentially harmful substances.
This requirement explains why many compounds that show promise in laboratory studies may not translate to real-world cognitive benefits.
Effective nootropics have been specifically designed or naturally evolved to penetrate this barrier and reach brain tissue where they can exert their cognitive-enhancing effects.
Types of Nootropics: Natural, Synthetic, and Prescription
Natural Nootropics
Natural nootropics include herbs, amino acids, vitamins, and other compounds found in nature.
They typically have milder effects but better safety profiles and are widely available as dietary supplements.
| Natural Nootropic | Primary Benefits | Typical Dosage | Safety Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | Alertness, focus, reaction time | 40-300 mg | High |
| L-Theanine | Calm focus, creativity | 50-200 mg | High |
| Bacopa Monnieri | Memory, learning | 300-600 mg | High |
| Rhodiola Rosea | Stress reduction, mental fatigue | 100-400 mg | High |
| Ginkgo Biloba | Memory, circulation | 120-240 mg | Moderate |
Synthetic Nootropics
Synthetic nootropics are laboratory-created compounds designed specifically for cognitive enhancement.
The most well-known family is the racetams, which includes piracetam, oxiracetam, and aniracetam.
Important: Synthetic nootropics are not FDA-approved for cognitive enhancement in healthy individuals and may carry unknown long-term risks. Recent studies have found unapproved drugs in many commercial products.
Common Synthetic Nootropics:
- Piracetam – The original racetam, studied for memory enhancement
- Noopept – Fast-acting synthetic with potential neuroprotective effects
- Phenylpiracetam – Stimulating racetam with physical performance benefits
- Alpha-GPC – Choline source for acetylcholine production
Prescription Nootropics
Prescription nootropics are FDA-approved medications primarily designed to treat specific medical conditions but sometimes used off-label for cognitive enhancement.
Warning: Using prescription medications without a prescription is illegal and potentially dangerous. These drugs should only be used under medical supervision for approved conditions.
Common Prescription Nootropics:
- Modafinil (Provigil) – Wakefulness-promoting agent for narcolepsy
- Adderall – Amphetamine-based ADHD medication
- Ritalin (Methylphenidate) – Stimulant for ADHD and narcolepsy
- Memantine (Namenda) – Alzheimer’s disease treatment
Proven Benefits of Nootropics
Scientific research has demonstrated several cognitive benefits of nootropics, though the strength of evidence varies significantly between different compounds and populations studied.
Evidence-Based Cognitive Benefits
Enhanced Memory
Improved formation, consolidation, and recall of memories.
Best evidence: Bacopa monnieri, caffeine + L-theanine
Increased Focus
Better sustained attention and reduced distractibility.
Best evidence: Caffeine, modafinil, methylphenidate
Reduced Mental Fatigue
Decreased cognitive exhaustion and improved endurance.
Best evidence: Rhodiola rosea, creatine
Enhanced Creativity
Improved divergent thinking and problem-solving.
Best evidence: L-theanine, microdosed psychedelics
Clinical Research Findings
Recent systematic reviews and meta-analyses have provided insights into nootropic effectiveness:
- A comprehensive 2022 study found that caffeine + L-theanine combinations consistently improved attention and reduced mind-wandering in healthy adults
- Multiple trials demonstrate Bacopa monnieri enhances memory formation when taken for 8-12 weeks
- Creatine supplementation shows significant cognitive benefits in vegetarians and sleep-deprived individuals
- Rhodiola rosea reduces mental fatigue by 20-30% in stressed populations
Population-Specific Benefits
Nootropic effectiveness often depends on the user’s baseline cognitive state and specific needs:
Students and Young Adults
- Improved study endurance and information retention
- Enhanced test performance under stress
- Better sleep quality with certain adaptogens
Working Professionals
- Increased productivity and task switching
- Reduced decision fatigue
- Better stress management
Older Adults
- Slowed age-related cognitive decline
- Improved processing speed
- Enhanced quality of life measures
Risks and Side Effects
While many nootropics have favorable safety profiles, all substances carry potential risks.
Understanding these risks is crucial for making informed decisions about cognitive enhancement.
Common Side Effects by Category
Natural Nootropics
- Caffeine: Jitters, insomnia, anxiety, dependence
- Ginkgo: Bleeding risk, headaches, digestive upset
- Ginseng: Overstimulation, insomnia, blood pressure changes
- Bacopa: Digestive issues, fatigue (initial weeks)
Synthetic Nootropics
- Racetams: Headaches, irritability, insomnia
- Noopept: Irritability, fatigue, brain fog (some users)
- Unknown compounds: Unpredictable effects due to lack of research
Prescription Stimulants (Off-label use)
- Cardiovascular: Increased heart rate, blood pressure
- Psychiatric: Anxiety, mood changes, psychosis (rare)
- Physical: Appetite suppression, sleep disruption
- Addiction potential: Tolerance, dependence, withdrawal
Serious Safety Concerns
Product Contamination and Mislabeling
A comprehensive 2020 FDA study found that 83% of brain health supplements contained unlisted compounds, while 67% were missing listed ingredients. Contamination risks include:
- Undisclosed stimulants and pharmaceutical drugs
- Heavy metals and toxic compounds
- Incorrect dosages of active ingredients
- Allergens not listed on labels
Long-term Risks and Unknown Effects
Many nootropics lack long-term safety data, particularly in healthy populations:
- Tolerance development: Reduced effectiveness over time requiring higher doses
- Withdrawal effects: Cognitive rebound when discontinuing use
- Unknown interactions: Unpredictable effects when combining multiple substances
- Developmental concerns: Potential impacts on brain development in young users
High-Risk Populations
Certain groups face elevated risks from nootropic use:
Contraindicated Groups
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- Children and adolescents
- Individuals with cardiovascular disease
- Those with psychiatric conditions
Requires Medical Supervision
- Individuals taking medications
- Those with liver or kidney disease
- People with bleeding disorders
- Individuals with sleep disorders
How to Use Nootropics Safely
Safe nootropic use requires careful planning, gradual implementation, and ongoing monitoring.
Following evidence-based safety protocols can minimize risks while maximizing potential benefits.
Essential Safety Principles
The “Start Low, Go Slow” Approach
- Begin with the lowest effective dose
- Introduce only one new substance at a time
- Allow 2-4 weeks to assess effects before adjusting
- Keep detailed logs of dosages and effects
- Take regular breaks to prevent tolerance
Pre-Use Health Assessment
Before starting any nootropic regimen, conduct a thorough health evaluation:
Medical History Review
- Current medications and supplements
- Known allergies and sensitivities
- Cardiovascular and psychiatric history
- Sleep patterns and disorders
Baseline Cognitive Assessment
- Memory and attention tests
- Mood and energy levels
- Sleep quality measures
- Stress and anxiety levels
Quality Control and Source Verification
Given the high rate of product contamination, choosing reputable sources is critical:
Red Flags to Avoid
- Products with proprietary blends (hidden dosages)
- Unrealistic claims like “instant genius” or “limitless pills”
- No third-party testing certificates
- Extremely low prices compared to competitors
- Products sold exclusively through MLM schemes
Quality Indicators
- Third-party testing for purity and potency
- Clear ingredient lists with specific dosages
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) certification
- Transparent company information and contact details
- Scientific references for product claims
Monitoring and Adjustment Protocol
Systematic monitoring helps optimize benefits while detecting potential problems early:
| Timeframe | Monitoring Focus | Action Items |
|---|---|---|
| Days 1-7 | Acute side effects, tolerance | Daily symptom log, vital signs if indicated |
| Weeks 2-4 | Cognitive effects, sleep impact | Weekly cognitive assessments, sleep tracking |
| Month 2-3 | Long-term benefits, tolerance | Monthly comprehensive review, dosage optimization |
| Ongoing | Sustained effects, health markers | Quarterly breaks, annual health checkups |
Dosage Recommendations and Stacking
Proper dosing is crucial for nootropic safety and effectiveness.
Individual responses vary significantly, making personalized approaches essential for optimal results.
Evidence-Based Dosage Guidelines
| Nootropic | Starting Dose | Effective Range | Maximum Safe Dose | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | 50 mg | 100-200 mg | 400 mg/day | Morning, pre-workout |
| L-Theanine | 100 mg | 100-200 mg | 600 mg/day | With caffeine or evening |
| Bacopa Monnieri | 150 mg | 300-600 mg | 900 mg/day | With meals, consistent timing |
| Rhodiola Rosea | 100 mg | 200-400 mg | 600 mg/day | Empty stomach, morning |
| Creatine | 3 g | 3-5 g | 10 g/day | Any time, consistent |
Nootropic Stacking Strategies
Stacking refers to combining multiple nootropics to achieve synergistic effects.
While potentially more effective, stacking increases complexity and risk.
Beginner-Friendly Stacks
Focus and Alertness Stack
- Caffeine: 100-150 mg
- L-Theanine: 150-200 mg
- Benefits: Smooth energy, reduced jitters, enhanced focus
- Timing: Morning or pre-work
Memory and Learning Stack
- Bacopa Monnieri: 300 mg
- Alpha-GPC: 300 mg
- Benefits: Enhanced memory formation and recall
- Timing: With breakfast, consistent daily use
Stress and Recovery Stack
- Rhodiola Rosea: 300 mg
- Ashwagandha: 300-500 mg
- Benefits: Reduced stress, improved resilience
- Timing: Morning (Rhodiola), evening (Ashwagandha)
Cycling and Tolerance Management
Regular breaks prevent tolerance development and maintain long-term effectiveness:
Recommended Cycling Protocols
- Stimulants (caffeine): 5 days on, 2 days off weekly
- Adaptogens: 8 weeks on, 2 weeks off
- Racetams: 6 weeks on, 2 weeks off
- Comprehensive stacks: 3 months on, 1 month off
FDA Regulation and Quality Control
Understanding the regulatory landscape is crucial for making informed decisions about nootropic supplements and avoiding potentially dangerous products.
Current Regulatory Framework
The FDA regulates nootropics differently based on their classification:
Prescription Drugs
- Rigorous pre-market testing
- FDA approval required
- Ongoing safety monitoring
- Quality guaranteed
Dietary Supplements
- No pre-market approval
- Self-regulated by manufacturers
- FDA acts only after problems
- Variable quality control
Unregulated Compounds
- No safety oversight
- Unknown purity/potency
- Legal status unclear
- High contamination risk
Quality Control Challenges
Recent investigations have revealed significant quality control issues in the nootropics market:
FDA Study Findings (2020)
Analysis of 12 popular brain health supplements revealed alarming quality control failures:
- 83% contained unlisted compounds
- 67% were missing listed ingredients
- 92% failed basic safety standards
- 58% used proprietary blends hiding actual dosages
Identifying Quality Products
Given regulatory limitations, consumers must take responsibility for product verification:
Third-Party Testing Certifications
- NSF International: Comprehensive purity and potency testing
- USP Verified: United States Pharmacopeia standards
- ConsumerLab: Independent supplement testing
- Informed Sport: Banned substance screening for athletes
Legal Considerations
The legal status of nootropics varies by jurisdiction and specific compound:
- United States: Most natural nootropics legal as supplements, synthetic compounds in legal gray area
- European Union: Stricter regulations, many synthetic nootropics require prescriptions
- Canada: Natural Health Product regulations apply, some synthetics prohibited
- Australia: Therapeutic Goods Administration oversight, prescription required for many compounds
How to Choose the Right Nootropics
Selecting appropriate nootropics requires careful consideration of individual goals, health status, lifestyle factors, and risk tolerance.
Goal-Based Selection Framework
For Enhanced Focus and Productivity
Recommended Options:
- Caffeine + L-Theanine (immediate effects)
- Rhodiola Rosea (stress-related focus issues)
- Modafinil (prescription, severe cases)
Considerations:
- Tolerance to stimulants
- Work schedule and timing
- Sleep impact
For Memory and Learning
Recommended Options:
- Bacopa Monnieri (long-term memory)
- Alpha-GPC (working memory)
- Creatine (reasoning and processing)
Considerations:
- Time to see effects (weeks to months)
- Consistent daily dosing required
- Baseline cognitive function
For Stress and Anxiety Management
Recommended Options:
- L-Theanine (acute anxiety)
- Ashwagandha (chronic stress)
- Rhodiola Rosea (stress resilience)
Considerations:
- Underlying anxiety disorders
- Medication interactions
- Lifestyle stress factors
Individual Assessment Checklist
Before selecting nootropics, complete this comprehensive self-assessment:
Health and Safety Factors
Medical History:
- Current medications
- Known allergies
- Cardiovascular conditions
- Mental health history
Lifestyle Factors:
- Sleep quality and duration
- Stress levels
- Diet and exercise habits
- Caffeine tolerance
Budget and Accessibility Considerations
Nootropic costs vary significantly, and sustainable use requires budget planning:
| Category | Monthly Cost Range | Accessibility | Quality Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basic Natural Stack | $20-50 | High | Variable |
| Premium Natural Stack | $75-150 | High | Good |
| Synthetic Compounds | $30-100 | Moderate | Poor |
| Prescription Options | $100-500+ | Low | Excellent |
Frequently Asked Questions
Are nootropics safe for daily use?
Natural nootropics like caffeine, L-theanine, and Bacopa monnieri are generally safe for daily use when taken at recommended dosages. However, synthetic compounds and prescription medications carry higher risks and should be used with caution and medical supervision.
How long does it take for nootropics to work?
Effects vary by compound: stimulants like caffeine work within 30-60 minutes, while herbs like Bacopa monnieri require 8-12 weeks of consistent use. Synthetic nootropics typically show effects within days to weeks.
Can I combine multiple nootropics safely?
Combining nootropics (stacking) can be safe when done gradually and systematically. Start with well-researched combinations like caffeine + L-theanine, introduce one new compound at a time, and monitor for interactions or side effects.
Do nootropics cause addiction or dependence?
Most natural nootropics have low addiction potential. However, stimulant-based compounds (caffeine, prescription medications) can cause physical dependence. Cycling usage and taking regular breaks helps prevent tolerance and dependence.
Are nootropics regulated by the FDA?
Prescription nootropics are strictly regulated, while dietary supplements receive minimal oversight. The FDA does not test supplements for safety or efficacy before market release, making third-party testing crucial for quality assurance.
What’s the difference between natural and synthetic nootropics?
Natural nootropics are derived from plants and have longer safety histories but milder effects. Synthetic nootropics are laboratory-created for specific cognitive effects but have less safety data and higher risk profiles.
Can students safely use nootropics for studying?
Students can safely use certain natural nootropics like caffeine, L-theanine, and Bacopa monnieri. However, prescription stimulants without medical supervision are dangerous and illegal. Focus on sleep, nutrition, and study techniques first.
Do nootropics work for everyone?
Individual responses to nootropics vary significantly based on genetics, baseline cognitive function, health status, and lifestyle factors. What works for one person may not work for another, making personalized approaches essential.
Conclusion
Nootropics represent a rapidly evolving field with significant potential for cognitive enhancement, but they require careful, informed use to maximize benefits while minimizing risks.
The $18.48 billion market reflects growing interest in cognitive optimization, yet quality control issues and regulatory gaps demand consumer vigilance.
Key takeaways for safe and effective nootropic use:
- Start with well-researched natural compounds like caffeine, L-theanine, and Bacopa monnieri
- Prioritize third-party tested products from reputable manufacturers
- Begin with low doses and introduce one compound at a time
- Maintain detailed logs to track effects and optimize dosing
- Take regular breaks to prevent tolerance and assess baseline function
- Consult healthcare providers, especially if taking medications or having health conditions
Remember that nootropics are tools to enhance an already healthy lifestyle, not replacements for proper sleep, nutrition, exercise, and stress management.
The most effective cognitive enhancement strategy combines evidence-based supplementation with fundamental wellness practices.