MCT oil is a purified supplement containing medium-chain triglycerides, a unique type of fat that is metabolized differently from most other fats in your diet.
Unlike long-chain fats, MCTs are rapidly absorbed and transported directly to the liver, where they are efficiently converted into energy or ketones.
This rapid conversion process is why interest in MCT oil has surged, particularly within the wellness and ketogenic diet communities.
In fact, a 2024 meta-analysis suggests that diets enriched with MCTs can be more effective for weight reduction compared to those with standard dietary fats.
This guide delves into the science-backed benefits, practical uses, and important safety considerations of incorporating MCT oil into your health regimen.
Read on to discover if this popular supplement is right for you.
In This Article
What Exactly Is MCT Oil? A Deep Dive into the Science
To truly understand the buzz around MCT oil, we need to look at its chemical structure and how our bodies handle it.
It’s not just another oil, its unique properties are rooted in basic biochemistry.
Understanding Fats: Triglycerides and Fatty Acid Chains
Most of the fats we consume, whether from olive oil, avocados, or butter, are in the form of triglycerides.
A triglyceride molecule is made of a glycerol backbone attached to three fatty acid chains.
The length of these chains—determined by the number of carbon atoms they contain—is what dictates how the fat is digested, absorbed, and used by the body.
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs): Fewer than 6 carbon atoms.
- Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFAs): Between 6 and 12 carbon atoms.
- Long-Chain Fatty Acids (LCFAs): More than 12 carbon atoms.
The vast majority of dietary fats are LCFAs, which require a more complex digestive process involving bile and pancreatic enzymes before they can be absorbed and used for energy or stored.
The Four Types of Medium-Chain Triglycerides
MCTs are categorized into four main types based on their carbon chain length. Each has slightly different properties:
- C6: Caproic Acid: The shortest MCT, it’s converted to ketones very quickly but is often excluded from supplements due to its unpleasant taste and smell.
- C8: Caprylic Acid: Considered the most ketogenic MCT, it is rapidly absorbed and converted into energy. High-quality MCT oils are often rich in C8.
- C10: Capric Acid: Also efficiently converted to ketones, though slightly slower than C8. It’s commonly found alongside C8 in MCT oil supplements.
- C12: Lauric Acid: The longest MCT, found in abundance in coconut oil. Some experts argue it behaves more like a long-chain fatty acid, as its absorption and metabolism are slower than C8 and C10.
How Your Body Metabolizes MCTs Differently
Herein lies the key to MCT oil benefits. Because of their shorter chain length, MCTs (especially C8 and C10) bypass the standard, lengthy digestive process required for LCFAs.
They are absorbed directly from the small intestine into the portal vein and sent straight to the liver.
This direct route means they are less likely to be stored as body fat and are instead rapidly converted into an immediate source of cellular energy.
This efficient metabolic pathway is what makes MCT oil a popular supplement for quick energy.
The Role of Ketones: An Alternative Fuel Source
In the liver, MCTs can be converted into molecules called ketones. Ketones are a highly efficient alternative fuel source for the body and, importantly, the brain, which typically relies on glucose.
When carbohydrate intake is low (as in a ketogenic diet) or when MCTs are consumed, the body produces ketones.
These ketones can cross the blood-brain barrier, providing the brain with a clean and stable energy supply.
This is a central reason for MCT oil’s growing reputation in supporting cognitive health.
What Are the Proven Benefits of MCT Oil?
While MCT oil is not a cure-all, a growing body of scientific research points to several potential health benefits, particularly in the areas of weight management, energy production, and brain health.
May Support Weight Management and Fat Loss
One of the most researched mct oil benefits is its potential role in weight management. Several mechanisms contribute to this effect:
- Increased Satiety: Studies suggest MCTs may increase the release of hormones like peptide YY and leptin, which promote feelings of fullness and can lead to reduced calorie intake.
- Higher Thermic Effect: The body may burn more calories processing MCTs compared to LCFAs, a phenomenon known as diet-induced thermogenesis. This means more energy is expended during digestion.
- Less Fat Storage: Due to their rapid conversion to energy, MCTs are less likely to be stored in fat cells compared to LCFAs, especially when consumed as a replacement for other fats.
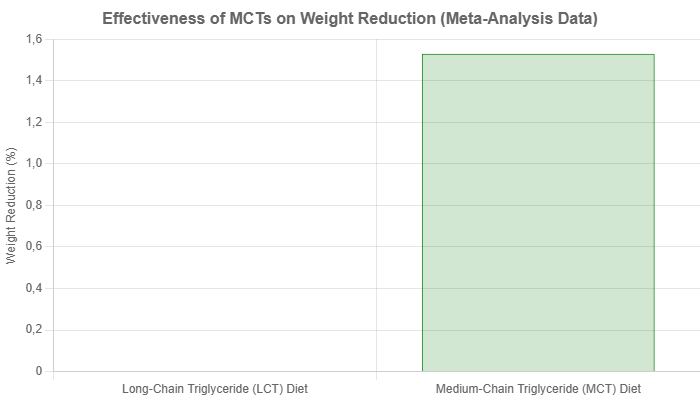
A 2024 meta-analysis published in the Journal of Functional Foods concluded that diets enriched with MCTs are more effective in achieving weight reduction compared to diets with long-chain triglycerides. The study found a weighted mean difference of -1.53% in weight reduction for MCT groups. Source: Journal of Functional Foods
Provides a Rapid Source of Energy for Body and Brain
The unique metabolic pathway of MCTs makes them an excellent source of mct oil for energy.
Unlike glucose, which can cause spikes and crashes in blood sugar, the energy from MCTs is more sustained.
This makes it a favorite among athletes looking for a quick pre-workout fuel source and individuals seeking to combat the mid-afternoon slump without relying on caffeine or sugar.
Potential to Enhance Brain Function and Cognitive Health
The brain is an energy-intensive organ. In certain conditions, like Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment (MCI), the brain’s ability to use glucose can become impaired, leading to an “energy gap.”
Ketones from MCT oil can help bridge this gap.
A 2022 study on subjects with Alzheimer’s found that consistent, long-term intake of MCT oil helped stabilize cognition.
The researchers noted that a minimum dose of one tablespoon per day was associated with stabilization or improvement in cognitive scores. Source: Juby et al., 2022, Nutrients.
However, it’s crucial to be balanced.
A comprehensive 2024 systematic review concluded that while MCTs reliably boost ketone levels in the brain, this doesn’t always translate into measurable clinical improvements in dementia symptoms.
More high-quality research is needed to make definitive recommendations. Source: Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, 2024.
May Improve Exercise Performance and Endurance
The evidence here is mixed but promising.
The theory is that by providing a quick energy source, MCTs could help spare muscle glycogen (the body’s stored carbohydrates), potentially delaying fatigue during long-duration exercise.
Some older studies showed that athletes consuming MCTs could endure longer bouts of high-intensity exercise.
A 2018 animal study found that MCTs enhanced exercise endurance by increasing mitochondrial biogenesis—the creation of new mitochondria, which are the powerhouses of our cells. Source: PLoS One, 2018.
However, more recent human studies have shown minimal to no direct performance enhancement, indicating this benefit may not apply to everyone.
How Does MCT Oil Compare to Coconut Oil?
This is a common point of confusion. While MCT oil is derived from coconut (or palm) oil, they are not the same thing.
The difference lies in their composition and concentration.
Composition and Concentration: The Key Difference
Coconut oil is a whole food fat that contains both medium-chain and long-chain triglycerides.
About 54% of its fats are MCTs, but the majority of that is lauric acid (C12).
MCT oil, on the other hand, is a manufactured supplement.
Through a process called fractionation, the C8 and C10 fatty acids are extracted and concentrated.
A good MCT oil contains 100% C8 and C10, with little to no C12 or C6.
Metabolic Speed and Ketone Production
Because MCT oil is a pure concentration of the fastest-metabolizing MCTs (C8 and C10), it is significantly more ketogenic than coconut oil.
It provides a more rapid and potent boost in energy and ketone levels.
Lauric acid (C12) in coconut oil is processed more slowly, blunting the immediate ketogenic effect.
| Feature | MCT Oil | Coconut Oil |
|---|---|---|
| MCT Content | 100% Medium-Chain Triglycerides | ~54% Medium-Chain Triglycerides |
| Primary Fatty Acids | Caprylic (C8) and Capric (C10) | Lauric (C12), plus C8, C10, and LCFAs |
| Metabolic Pathway | Rapid, direct to liver | Slower, a mix of direct and standard digestion |
| Ketone Production | High and fast | Moderate and slower |
| Taste & Smell | Neutral, odorless | Distinct coconut flavor and aroma |
| Best Use | Supplement for energy, ketosis (not for high-heat cooking) | Cooking, baking, skin care |
How Do You Use MCT Oil Effectively?
Incorporating MCT oil into your routine is simple, but it’s important to start correctly to avoid potential side effects.
Finding the Right Dosage: Start Low, Go Slow
The golden rule for how to use mct oil is to begin with a small dose.
Taking too much too soon is the primary cause of the most common mct oil side effects.
- Start with 1 teaspoon (5 mL) per day. Take it with food to improve tolerance.
- Monitor your tolerance. If you experience no digestive upset, you can slowly increase the dose every few days.
- Work up to a target dose. Most studies use between 1 to 3 tablespoons (15-45 mL) per day, depending on individual goals and tolerance. A maximum daily dose of 4–7 tablespoons (60–100 mL) has been suggested, but it’s best to stay within a moderate range.
Practical Ways to Add MCT Oil to Your Diet
MCT oil is flavorless and odorless, making it easy to add to various foods and drinks.
Note that most MCT oils have a low smoke point and are not suitable for high-heat cooking.
- Bulletproof Coffee: Blend it into your morning coffee (with or without grass-fed butter/ghee) for a creamy, energy-boosting start to your day.
- Smoothies and Shakes: Add a spoonful to your protein shake or fruit smoothie.
- Salad Dressings: Use it as a base for homemade vinaigrettes.
- Drizzled Over Food: Drizzle it over vegetables, yogurt, or oatmeal after cooking.
Choosing a High-Quality MCT Oil
Not all MCT oils are created equal. Look for:
- Source: Choose one derived from 100% coconuts rather than palm oil, which has environmental concerns.
- Composition: Opt for a blend of C8 and C10, or pure C8 for the most potent ketogenic effect.
- Purity: Ensure it’s free from fillers, additives, and other oils.
Are There Any Side Effects or Risks?
MCT oil is generally considered safe for most people, but there are potential side effects and considerations to be aware of.
Common Gastrointestinal Issues and How to Avoid Them
The most frequently reported mct oil side effects are digestive. These include:
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramping
- Vomiting
These effects are dose-dependent.
They occur because the rapid influx of fat can draw water into the gut.
The “start low, go slow” approach and taking MCT oil with food are the best ways to prevent this.
Considerations for Specific Health Conditions
While MCTs can be beneficial, individuals with certain conditions should exercise caution.
High doses could potentially lead to fat accumulation in the liver over time, so those with pre-existing liver disease should consult a doctor before use.
People with uncontrolled type 1 diabetes should also be cautious due to the risk of ketoacidosis, although nutritional ketosis is different and generally safe.
The Debate on Cholesterol and Heart Health
The effect of MCT oil on cholesterol is complex and not fully settled.
Some studies show it can help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and increase HDL (“good”) cholesterol. However, other studies have reported increases in total cholesterol.
Because MCTs are a type of saturated fat, it’s wise for anyone with concerns about heart disease or cholesterol levels to monitor their blood lipids with a healthcare professional when supplementing with MCT oil.
Who Should Consider Taking MCT Oil?
MCT oil can be a valuable tool for specific groups of people:
- Individuals on a Ketogenic Diet: To help increase ketone levels, ease the transition into ketosis, and provide a quick energy source.
- Athletes: Particularly endurance athletes who may benefit from a non-carbohydrate energy source.
- People Seeking Cognitive Support: Those interested in the potential brain-boosting benefits of ketones, especially older adults.
- Anyone Looking for a Quick Energy Boost: As a healthy alternative to sugary drinks or excessive caffeine for combating fatigue.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About MCT Oil
1. Can I take MCT oil every day?
Yes, MCT oil can be taken daily. It’s best to start with a small dose and gradually increase to your desired amount to ensure good tolerance. Consistency is key for potential benefits.
2. Will MCT oil make me lose weight without dieting?
No. While MCT oil can support weight loss by increasing fullness and metabolism, it is not a magic pill. It works best when incorporated into a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
3. What’s the best time of day to take MCT oil?
Many people prefer taking it in the morning for an energy boost or before a workout. Taking it with a meal can help minimize potential digestive side effects.
4. Does MCT oil break a fast?
Yes. MCT oil contains calories and is a source of fat, so consuming it will technically break a fast. However, some people use it during a fasting window as it doesn’t spike insulin.
5. Can I cook with MCT oil?
It is not recommended for high-heat cooking. Most MCT oils have a low smoke point (around 320°F or 160°C), and heating it beyond this point can destroy the beneficial fats and create harmful compounds.
6. Is MCT oil better than coconut oil for keto?
Yes. Due to its higher concentration of C8 and C10 fatty acids, MCT oil is more effective at raising ketone levels quickly, making it a more potent supplement for the ketogenic diet.
7. How long does it take to feel the effects of MCT oil?
The energy-boosting effects can often be felt within 30 to 60 minutes as the MCTs are rapidly converted to energy. Long-term benefits, like cognitive support, may take weeks or months of consistent use.
8. Can MCT oil cause liver damage?
In healthy individuals at recommended doses, there is no strong evidence that MCT oil causes liver damage. However, very high doses over a long period could theoretically contribute to fat buildup in the liver.
Conclusion
MCT oil is a unique and powerful supplement with a strong scientific basis for its benefits. Its ability to provide rapid energy, support ketone production, and potentially aid in weight management and cognitive health makes it a compelling addition to a wellness routine.
However, it’s essential to approach it with realistic expectations. It is a tool to enhance a healthy lifestyle, not a replacement for one.
The most significant benefits are seen when it’s used to complement a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Remember to start with a small dose, choose a high-quality product, and listen to your body.
If you are considering adding MCT oil to your regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions, it is always best to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to ensure it’s a safe and appropriate choice for you.
Have you tried MCT oil? Share your experience or questions in the comments below!
Reference
[1] Coconut-sourced MCT oil: its potential health benefits beyond …
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11101-024-09969-1
[2] Effects of Medium-Chain Triglycerides on Weight Loss and Body …
https://www.jandonline.org/article/S2212-2672(14)01591-3/fulltext
[3] MCT Oil vs Coconut Oil – Citrin Foundation
https://citrinfoundation.org/mct-oil-vs-coconut-oil
[4] Use of medium chain triglyceride (MCT) oil in subjects with …
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8919247
[5] 7 Science-Based Benefits of MCT Oil – Healthline
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/mct-oil-benefits
[6] Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) for the Symptomatic Treatment …
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11074881
[7] Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Use of MCT …
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8624628
[8] Supplementation with medium-chain fatty acids increases body …
https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-023-03880-7
[9] What Is MCT Oil and Do You Need More of It? – Triathlete
https://www.triathlete.com/nutrition/what-is-mct-oil-and-do-you-need-more-of-it/
[10] What is the difference between MCT and coconut oil?
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/mct-oil-vs-coconut-oil

