Can you truly boost your metabolism with the food you eat?
The science says yes. Certain foods for boosting metabolism work by increasing the “thermic effect of food” (TEF), which is the energy your body expends to digest, absorb, and process nutrients.
While metabolism is complex, influenced by genetics, age, and activity level, strategic food choices can provide a significant edge in your health and weight management journey.
In fact, research shows that protein, the most thermogenic macronutrient, can temporarily increase your metabolic rate by up to 30%.
This article delves into 15 scientifically-backed foods that can help fire up your metabolic engine, enhance fat burning, and support your overall well-being.
We’ll explore not just *what* to eat, but *why* it works, providing you with practical, evidence-based strategies to make a real difference.
In This Article
What is Metabolism and Why Does It Matter?
Metabolism is a term that describes all the chemical reactions in your body that keep you alive.
These processes convert the food and drink you consume into energy.
Understanding its components is the first step toward influencing it, and choosing the right foods for boosting metabolism is a powerful way to do so.
Defining Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Total Energy Expenditure (TEE)
Your metabolism is more than just one number.
It’s a combination of factors that make up your Total Energy Expenditure (TEE), or the total number of calories you burn each day. TEE is primarily composed of three parts:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR): This is the energy your body uses at rest to maintain vital functions like breathing, circulation, and cell production. It accounts for the largest portion of your daily calorie burn, typically 60-75%.
- Physical Activity: This is the energy burned during exercise and any other physical movement throughout the day. It’s the most variable component of your TEE.
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF): This is the energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize the food you eat. While it’s the smallest component (around 10% of TEE), it’s the one we can most directly influence with with a diet rich in foods for boosting metabolism.
The Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
The TEF is where our dietary strategy comes into play.
Different macronutrients require different amounts of energy to be processed. This is a key reason why certain foods for boosting metabolism are so effective.
According to a study published in Nutrition & Metabolism, the main determinants of diet-induced thermogenesis are the energy content and the protein fraction of the diet. This highlights protein’s superior role in elevating metabolic rate post-meal.
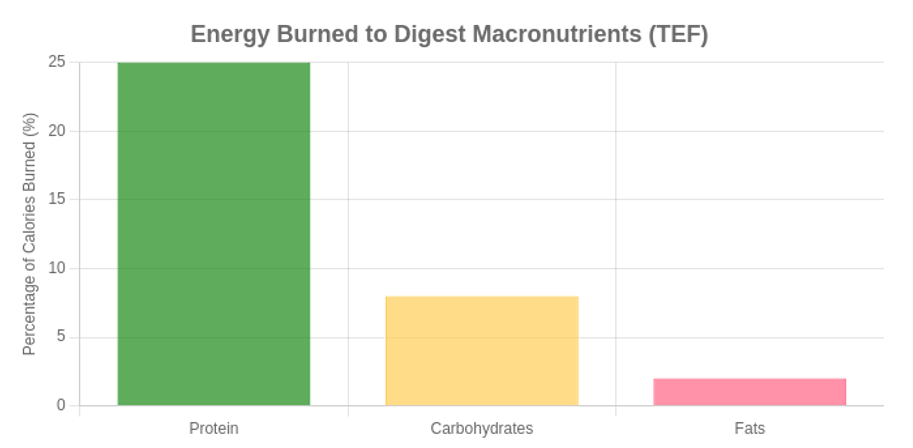
Here’s a breakdown of the approximate TEF for each macronutrient:
- Protein: 20-30%
- Carbohydrates: 5-10%
- Fats: 0-3%
This means that for every 100 calories of protein you consume, your body uses 20-30 of those calories just to process it.
This is significantly higher than for carbs and fats, making high-protein foods a cornerstone of any metabolism-focused diet.
The 15 Best Foods for Boosting Your Metabolism
Now, let’s dive into the specific foods for boosting metabolism that leverage these metabolic principles to help you achieve your health goals.
1. Protein-Rich Foods (Lean Meats, Fish, Eggs)
Why it works: As established, protein has the highest TEF. Consuming it forces your body to work harder, burning more calories.
Furthermore, protein is crucial for building muscle, and since muscle is more metabolically active than fat, having more muscle increases your BMR.
This makes lean protein one of the most effective foods for boosting metabolism.
Scientific Evidence: A review in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition concluded that higher protein intake significantly increases thermogenesis and satiety compared to lower protein diets.
Practical Tip: Aim to include a source of lean protein like chicken breast, turkey, salmon, or eggs in every meal to keep your metabolic rate elevated throughout the day.
2. Legumes and Beans
Why it works: Legumes like lentils, chickpeas, and black beans are a powerhouse of protein and dietary fiber. The combination of these two nutrients makes them particularly effective.
The protein provides a high TEF, while the resistant starch and fiber are difficult to digest, further increasing the energy required for processing and promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
Scientific Evidence: WebMD highlights that the high fiber content in legumes forces your metabolism to work harder and helps you feel full longer, preventing overeating.
Practical Tip: Add a cup of black beans to your salad, make a lentil soup, or enjoy hummus (made from chickpeas) as a snack.
3. Chili Peppers
Why it works: The heat in chili peppers comes from a compound called capsaicin, a compound with thermogenic properties that can slightly increase calorie-burning
While the effect is modest, chili peppers are still valuable foods for boosting metabolism.
It may also increase fat oxidation and reduce appetite.
Scientific Evidence: Research published in Appetite found that capsaicin consumption can promote negative energy balance by increasing energy expenditure and reducing hunger.
Practical Tip: Sprinkle red pepper flakes on your pizza or pasta, or add fresh jalapeños to your stir-fry. Even a small amount can provide a metabolic nudge.
4. Green Tea
Why it works: Green tea is one of the most well-researched metabolism-boosting beverages. Its power comes from a combination of caffeine and potent antioxidants called catechins, particularly epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG).
Together, they help stimulate the nervous system and increase thermogenesis and fat oxidation.
Scientific Evidence: A meta-analysis in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggested that green tea extract can play a role in body composition control through sympathetic activation of thermogenesis and fat oxidation.
Practical Tip: Swap one of your daily sugary drinks for a cup of unsweetened green tea. For best results, aim for 3-4 cups per day.
5. Coffee
Why it works: The caffeine in coffee is a well-known stimulant that can directly increase your BMR by mobilizing fats from fat tissues.
This direct impact on BMR solidifies coffee’s place on the list of top foods for boosting metabolism.
This effect can also enhance physical performance.
Scientific Evidence: A 2024 study highlighted by the Endocrine Society found that moderate coffee intake is associated with a lower risk of cardiometabolic diseases, partly due to its metabolic effects.
Practical Tip: Enjoy a cup of black coffee before a workout to maximize its fat-burning potential. Avoid adding excessive sugar or cream, which can negate the benefits.
6. Berries
Why it works: Berries like blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are packed with fiber and powerful antioxidants called polyphenols.
While not direct thermogenic agents, they support metabolic health by reducing inflammation and improving insulin sensitivity.
A body with less inflammation and better blood sugar control is a more efficient metabolic machine.
Scientific Evidence: Research in Molecules suggests that the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of blueberry components contribute to well-regulated glucose metabolism.
Practical Tip: Add a handful of mixed berries to your morning yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothie for a nutrient-dense, metabolism-supporting start to your day.
7. Whole Grains
Why it works: Unlike refined grains, whole grains like oats, brown rice, and quinoa contain their entire grain kernel, including the fiber-rich bran and nutrient-packed germ.
Your body has to expend more energy to break down these complex carbohydrates and fiber, resulting in a higher TEF compared to processed carbs.
Scientific Evidence: Harvard Health notes that fiber-rich, unrefined carbohydrates can increase energy expenditure because they take longer to digest.
Practical Tip: Swap white bread for 100% whole-wheat bread, white rice for quinoa or brown rice, and sugary cereals for a bowl of oatmeal.
8. Ginger
Why it works: Ginger contains gingerol, which has thermogenic properties.
It can increase body temperature and may help control appetite.
While research is ongoing, it’s a promising addition to your list of foods for boosting metabolism.
Scientific Evidence: While more human studies are needed, preliminary research suggests ginger can enhance the thermic effect of food and promote feelings of satiety.
Practical Tip: Add fresh grated ginger to stir-fries, soups, or brew it into a soothing tea with lemon.
9. Seaweed
Why it works: Seaweed is a rare dietary source of iodine, a mineral that is absolutely essential for the proper functioning of your thyroid gland.
The thyroid produces hormones that regulate your metabolism.
An iodine deficiency can lead to a sluggish thyroid (hypothyroidism) and a slowed metabolic rate.
Scientific Evidence: The link between iodine and thyroid function is well-established in medical science. Maintaining adequate iodine levels is critical for metabolic health.
Practical Tip: Add nori sheets to your meals, sprinkle kelp flakes as a salt substitute, or enjoy a wakame salad.
10. Nuts and Seeds
Why it works: Nuts and seeds (like almonds, walnuts, and chia seeds) offer a triple-threat for metabolism: protein, fiber, and healthy fats.
This combination promotes satiety, has a decent TEF from the protein, and provides sustained energy.
Scientific Evidence: As noted by Ochsner Health, protein-rich foods can help boost metabolism, like nuts and seeds, because they require more energy for digestion.
Practical Tip: A small handful of almonds makes a great afternoon snack. Sprinkle chia or flax seeds into your smoothie or on top of your yogurt.
11. MCT Oil & Coconut Oil
Why it works: Medium-Chain Triglycerides (MCTs) are metabolized differently, sent directly to the liver and readily converted to energy, which can slightly increase thermogenesis.
This unique metabolic pathway makes them interesting foods for boosting metabolism.
Scientific Evidence: A review in Foods discusses the unique metabolic pathways of MCTs, which have been researched for their potential applications in weight management since the 1950s.
Practical Tip: Use coconut oil for cooking at medium heat or add a teaspoon of MCT oil to your morning coffee or smoothie. Use in moderation as it is still a calorie-dense fat.
12. Apple Cider Vinegar
Why it works: While not a powerful thermogenic, apple cider vinegar (ACV) may support metabolism indirectly.
Some studies suggest it can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar responses after meals. It may also increase feelings of fullness, leading to lower overall calorie intake.
Scientific Evidence: The evidence is mixed but promising in some areas. The primary benefit seems to be related to satiety and blood sugar regulation rather than a direct metabolism boost.
Practical Tip: Mix 1-2 tablespoons of ACV in a large glass of water and drink it before a meal. Never drink it straight, as its acidity can damage tooth enamel and your esophagus.
13. Cruciferous Vegetables
Why it works: Vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale are high in fiber and water, making them filling and low in calories.
They also contain B vitamins and other nutrients that are essential cofactors in metabolic reactions.
Their high fiber content also means your body works a bit harder to digest them.
Scientific Evidence: Nuvance Health lists broccoli and kale among foods packed with essential nutrients that support a healthy metabolism.
Practical Tip: Roast broccoli with a sprinkle of chili flakes, add kale to your smoothie, or use cauliflower rice as a low-carb base for meals.
14. Water
Why it works: Water is fundamental. Every energy-burning reaction requires it, and dehydration slows metabolism.
Though not a “food,” proper hydration is the foundation that makes all other foods for boosting metabolism effective.
Practical Tip: Carry a reusable water bottle with you and aim for at least 8 glasses (about 2 liters) per day, or more if you are active.
15. Cacao and Dark Chocolate
Why it works: Good news for chocolate lovers! Cacao and dark chocolate (with 70% or higher cacao content) are rich in flavanols and contain small amounts of caffeine and theobromine, which can have a mild stimulatory effect on the metabolism.
The flavanols may also help improve blood flow and insulin sensitivity.
Scientific Evidence: The benefits are more related to cardiovascular health and insulin function, which are pillars of a healthy metabolic system, rather than a large, direct thermogenic effect.
Practical Tip: Enjoy a small square of high-quality dark chocolate as a dessert or add unsweetened cacao powder to your smoothies or coffee.
Beyond the Plate: How to Create a Pro-Metabolism Lifestyle
While these foods can help, they work best as part of a holistic strategy.
True metabolic health is built on a foundation of consistent, healthy habits.
The Psychology of Eating: Mindful Habits Over Calorie Counting
Obsessing over every calorie can be counterproductive and stressful. Instead, focus on mindful eating.
Pay attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Eating slowly and without distractions can improve digestion and increase satisfaction, preventing overconsumption.
This approach fosters a healthier relationship with food, which is more sustainable than restrictive dieting.
Building a Metabolism-Boosting Meal Plan
Here’s what a day of metabolism-supporting meals, incorporating many of the best foods for boosting metabolism, could look like:
- Breakfast: Scrambled eggs (protein) with spinach (fiber, nutrients) and a side of whole-grain toast. A cup of green tea on the side.
- Lunch: A large salad with grilled chicken breast (protein), mixed greens, chickpeas (protein, fiber), and a light vinaigrette made with apple cider vinegar.
- Snack: A small handful of almonds (protein, healthy fats) and a piece of fruit like an apple or berries.
- Dinner: Baked salmon (protein, omega-3s) with roasted broccoli (fiber) and quinoa (protein, complex carbs).
The Role of Hydration and Sleep
As mentioned, staying hydrated is non-negotiable. Equally important is sleep.
A lack of quality sleep can disrupt hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, such as ghrelin and leptin.
It can also increase cortisol levels, a stress hormone linked to fat storage. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
Strength Training
If foods for boosting metabolism are the kindling, strength training is the fire.
Building lean muscle mass is the single most effective long-term strategy for increasing your BMR.
Muscle burns more calories at rest than fat does. Incorporate resistance training (using weights, bands, or your body weight) into your routine 2-3 times per week.
Comparative Analysis of Thermogenic Foods
To help you prioritize, here is a table comparing some of the top metabolism-boosting food categories.
| Food/Category | Active Compound(s) | Primary Mechanism | Scientific Backing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein-Rich Foods | Amino Acids | High Thermic Effect of Food (TEF), Muscle Maintenance | Very Strong |
| Chili Peppers | Capsaicin | Thermogenesis, Increased Fat Oxidation | Strong |
| Green Tea / Coffee | Caffeine, Catechins (EGCG) | CNS Stimulation, Thermogenesis, Fat Mobilization | Very Strong |
| Legumes & Whole Grains | Fiber, Protein, Complex Carbs | High TEF, Slow Digestion, Satiety | Strong |
| MCT Oil | Medium-Chain Triglycerides | Unique Metabolic Pathway, Increased Energy Expenditure | Moderate |
| Seaweed | Iodine | Supports Thyroid Hormone Production | Strong (for thyroid health) |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are answers to common questions about foods for boosting metabolism and how they fit into a healthy lifestyle.
1. Can I permanently speed up my metabolism?
You can’t permanently change your genetic baseline, but you can influence it long-term. Building more muscle through strength training is the most effective way to increase your resting metabolic rate (BMR) over time.
2. How long does it take for these foods to affect metabolism?
The thermic effect from these foods for boosting metabolism is temporary, occurring for a few hours after you eat. Consistent inclusion of these foods, combined with a healthy lifestyle, can lead to noticeable changes in body composition and energy levels over weeks and months.
3. Do metabolism-boosting supplements work?
Many supplements make bold claims but have little scientific backing. While some ingredients like caffeine and green tea extract are effective, they are best consumed from whole food/drink sources. Always consult a doctor before taking new supplements.
4. Will drinking cold water boost my metabolism?
Yes, but only slightly and temporarily. Your body must expend energy to warm the water to body temperature, a process called water-induced thermogenesis. The effect is minor, but staying hydrated is crucial for overall metabolic function.
5. Does eating small, frequent meals boost metabolism?
This is a common myth. Research shows that meal frequency has little to no effect on total daily energy expenditure. What matters most is the total amount and type of food you eat throughout the day.
6. Which macronutrient has the highest thermic effect?
Protein. Your body burns significantly more calories (20-30%) digesting protein compared to carbohydrates (5-10%) and fats (0-3%). This is a primary reason high-protein diets are effective for weight management.
7. Can I lose weight just by eating these foods?
While these foods can help, sustainable weight loss requires a comprehensive approach. This includes a balanced diet, maintaining a modest calorie deficit, regular physical activity (especially strength training), adequate sleep, and stress management.
8. Is green tea better than coffee for weight loss?
Both are effective and are considered top-tier foods for boosting metabolism (in beverage form). Coffee typically has more caffeine for a stronger immediate boost. Green tea has the synergistic benefit of caffeine plus EGCG. The best choice depends on your personal preference.
Conclusion
Boosting your metabolism isn’t about finding a single magic bullet, but about building a symphony of positive habits.
By strategically incorporating foods for boosting metabolism—especially those rich in protein, fiber, and unique compounds like capsaicin and catechins—you can enhance your body’s natural calorie-burning processes.
Remember, the most powerful results come from a holistic approach. Combine a nutrient-dense diet with regular strength training, consistent hydration, quality sleep, and mindful eating practices.
Start small. Pick two or three foods from this list and find creative ways to add them to your weekly meals.
As you build momentum, these small changes will compound, leading to a more efficient metabolism, better energy levels, and a healthier you.
What’s your favorite metabolism-boosting food or recipe? Share your thoughts and tips in the comments below to help our community!
References
[1] The truth about metabolism – Harvard Health
https://www.health.harvard.edu/staying-healthy/the-truth-about-metabolism
[2] Long-Term Intake of a High-Protein Diet Affects Body Phenotype …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022316622106413
[3] Artigo The 15 Best Foods for Boosting Metabolism and Burning Fat
[4] The 11 Best Foods to Boost Your Metabolism – Healthline
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/metabolism-boosting-foods
[5] Diet induced thermogenesis, older and newer data with …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2589936824000239
[6] The effects of high protein diets on thermogenesis, satiety … – PubMed
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15466943
[7] 12 Foods to Support Healthy Metabolism – Ochsner Blog
https://blog.ochsner.org/articles/metabolism-boosting-foods-and-spices
[8] The Effects of High Protein Diets on Thermogenesis, Satiety and …
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/07315724.2004.10719381
[9] Foods to Eat That Help Your Metabolism – WebMD
https://www.webmd.com/diet/ss/slideshow-foods-to-eat-that-help-your-metabolism
[10] The compound in hot chili peppers that can boost your …
[11] The effects of a thermogenic supplement on metabolic and …
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9987759
[12] Green Tea for Weight Loss: How it Works – Healthline
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/green-tea-and-weight-loss
[13] The effects of hedonically acceptable red pepper doses on …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0031938410004063
[14] Moderate coffee consumption is associated with lower risk of …
[15] Exploring Thermogenic Foods and Their Impact
[16] Moderate coffee and caffeine consumption is associated with lower …
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/09/240917125341.htm
[17] Recent Research on the Health Benefits of Blueberries and Their …
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7442370
[18] Can you increase your metabolism? – Harvard Health
https://www.health.harvard.edu/nutrition/can-you-increase-your-metabolism
[19] 12 Foods to Support Healthy Metabolism – Ochsner Blog
https://blog.ochsner.org/articles/metabolism-boosting-foods-and-spices

