To boost testosterone naturally involves a holistic approach focusing on diet, exercise, sleep, and stress management.
With testosterone levels declining by about 1-2% per year after age 30, and up to 40% of men over 45 experiencing low levels, understanding natural optimization is more crucial than ever.
This guide will delve into scientifically-backed lifestyle changes, nutrition strategies, effective exercises, and evidence-based supplements to help you optimize your hormonal health.
Testosterone is more than just a sex hormone, it’s a cornerstone of male vitality, influencing everything from muscle mass and mood to cognitive function and heart health. Optimizing it naturally is one of the most powerful investments you can make in your long-term well-being.
In This Article
What is Testosterone and Why Does It Matter?
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone, though women also produce it in smaller amounts. In men, it’s mainly produced in the testicles and is responsible for the development of male characteristics during puberty.
However, its role extends far beyond adolescence.
The Role of Testosterone in Men’s Health
Maintaining optimal testosterone levels is vital throughout a man’s life. It plays a crucial role in:
- Sex Drive (Libido): Testosterone is a key driver of sexual desire.
- Muscle Mass and Strength: It stimulates protein synthesis, helping to build and maintain muscle.
- Bone Density: Testosterone helps bones stay strong and dense, reducing the risk of osteoporosis.
- Fat Distribution: It influences where your body stores fat. Low levels can lead to increased body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Red Blood Cell Production: It stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells.
- Mood and Cognitive Function: Healthy levels are associated with better mood, confidence, and cognitive abilities like memory and spatial awareness.
Understanding the Natural Decline with Age
Testosterone levels typically peak in late adolescence and early adulthood.
After age 30 or 40, levels begin to decline gradually.
Research published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism indicates that total testosterone levels fall by an average of 1% to 2% per year.
This is a natural part of aging, but a steeper decline or prematurely low levels can significantly impact quality of life.
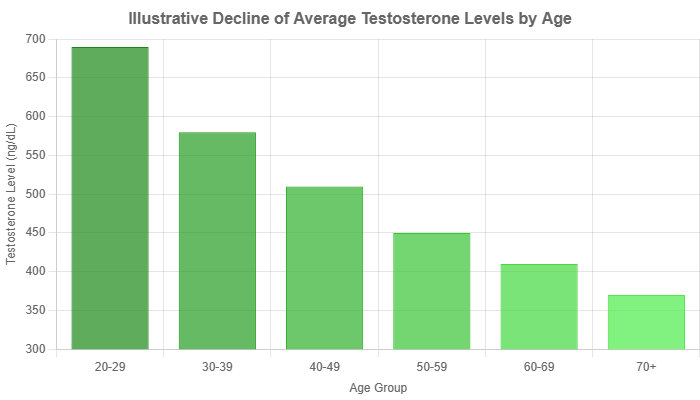
Chart illustrates the typical age-related decline in average testosterone levels in men. Individual levels can vary significantly.
How Do I Know If I Have Low Testosterone?
The symptoms of low testosterone (also known as male hypogonadism) can be subtle and are often mistaken for normal signs of aging.
Recognizing them is the first step toward taking action.
Common Signs and Symptoms of Low T
If you’re experiencing several of the following symptoms, it might be worth investigating your hormone levels.
According to the Urology Care Foundation, key signs include:
- Low Sex Drive: A noticeable drop in your desire for sexual activity.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and a lack of energy, even with adequate rest.
- Reduced Muscle Mass: Difficulty building or maintaining muscle, and a potential decrease in strength.
- Increased Body Fat: Particularly an increase in belly fat.
- Mood Changes: Irritability, depression, or a lack of focus and motivation.
- Hair Loss: Loss of body and facial hair.
The Importance of a Medical Diagnosis
While these symptoms are indicative, they can also be caused by other health issues.
The only way to confirm low testosterone is through a blood test.
A doctor will typically order a test for “total testosterone” levels, usually performed in the morning when levels are at their highest.
If your levels are low, your doctor can help determine the underlying cause and recommend the best course of action, whether it’s lifestyle changes or medical treatment.
Can Lifestyle Changes Really Boost Testosterone?
Absolutely. For many men, especially those with borderline low levels, foundational lifestyle habits are the most powerful and sustainable ways to boost testosterone.
These strategies work by creating an optimal internal environment for hormone production.
The Power of Sleep
Never underestimate the power of sleep.
Most testosterone is released during sleep, particularly during the deep REM stages.
Chronic sleep deprivation can crush your levels.
A landmark study from the University of Chicago found that restricting sleep to just five hours per night for one week decreased daytime testosterone levels by 10-15% in healthy young men.
That’s an effect equivalent to aging 10 to 15 years.
Actionable Tip: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Improve sleep hygiene by creating a dark, cool room, avoiding screens before bed, and maintaining a consistent sleep schedule.
Stress Management
Chronic stress is a testosterone killer.
When you’re constantly stressed, your body produces high levels of the hormone cortisol.
Cortisol and testosterone have an inverse relationship, when one goes up, the other tends to go down.
Research has shown that elevated cortisol can directly inhibit testosterone production.
Managing stress is not just for your mental health, it’s for your hormonal health too.
Effective stress-reduction techniques include meditation, deep breathing exercises, spending time in nature, and engaging in hobbies you enjoy.
Weight Management
Maintaining a healthy body weight is one of the most effective strategies for optimizing testosterone.
Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat (belly fat), contains high levels of the enzyme aromatase.
Aromatase converts testosterone into estrogen, the primary female sex hormone.
This means the more body fat you have, the more of your precious testosterone is being converted into estrogen, creating a vicious cycle.
Studies show that overweight and obese men have significantly lower testosterone levels than their leaner counterparts.
Limiting Alcohol and Environmental Estrogens
Excessive alcohol consumption can negatively impact testosterone production by affecting the testes and the hormonal signals from the brain.
While moderate consumption is unlikely to have a major effect, heavy or chronic drinking is detrimental.
Furthermore, try to minimize exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals like BPA (found in some plastics) and parabens, which can mimic estrogen in the body and potentially disrupt hormonal balance.
What is the Best Exercise to Increase Testosterone?
Exercise is a potent natural way to boost testosterone.
However, not all exercise is created equal.
The type, intensity, and duration of your workouts all play a role.
Resistance Training: The King of Testosterone-Boosting Workouts
If you could only choose one form of exercise to increase testosterone, it should be resistance training.
Lifting weights, especially using compound movements that engage large muscle groups (like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows), has been consistently shown to cause an acute increase in testosterone levels post-workout.
A review in Sports Medicine highlights that this hormonal response is a key factor in promoting muscle growth.
Focus on lifting heavy with adequate volume and intensity for the best results.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) vs. Steady-State Cardio
HIIT, involving short bursts of all-out effort and recovery, is another effective way to boost testosterone.
It’s a time-efficient way to improve cardiovascular fitness and hormonal health.
In contrast, while moderate cardio is excellent for heart health and weight management, excessive, long-duration endurance exercise (like marathon running) can sometimes lead to chronically elevated cortisol and lower testosterone levels.
The Risk of Overtraining
More is not always better.
Overtraining—pushing your body beyond its ability to recover—can lead to a state of chronic fatigue, elevated cortisol, and suppressed testosterone.
Listen to your body, prioritize rest and recovery days, and ensure your training program is sustainable.
Which Foods Genuinely Boost Testosterone?
Your diet provides the raw materials your body needs to produce hormones.
Focusing on the right foods that boost testosterone can provide essential nutrients for optimal production.
Macronutrients Matter: Balancing Protein, Carbs, and Healthy Fats
A well-balanced diet is key. Don’t fall for fad diets that eliminate entire macronutrient groups.
- Healthy Fats: Dietary fat, especially saturated and monounsaturated fats, is crucial for testosterone production. Cholesterol is a direct precursor to testosterone. Good sources include olive oil, avocados, nuts, and egg yolks.
- Protein: Adequate protein is necessary for maintaining muscle mass and aiding in fat loss, both of which support healthy testosterone levels.
- Carbohydrates: Carbs help fuel intense workouts and can help keep cortisol levels in check. Opt for complex carbs from whole food sources like potatoes, oats, and quinoa.
Key Micronutrients: The Role of Zinc and Magnesium
Two minerals are particularly important for testosterone:
- Zinc: This mineral is essential for the production of testosterone. A classic study showed that restricting zinc intake in healthy young men led to a significant drop in testosterone, while supplementing elderly men with a zinc deficiency nearly doubled their levels.
- Magnesium: This mineral is involved in hundreds of enzymatic reactions, including those related to testosterone. It can help reduce the binding of testosterone to Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin (SHBG), increasing the amount of “free” testosterone available to your body.
Top 10 Testosterone-Supporting Foods
- Oysters: The king of zinc-rich foods.
- Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel): Rich in Omega-3s and Vitamin D.
- Eggs: A great source of protein, healthy fats, and Vitamin D.
- Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale): Packed with magnesium.
- Avocados: Loaded with healthy monounsaturated fats.
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Another excellent source of healthy fats.
- Onions and Garlic: May help boost levels of luteinizing hormone, which signals testosterone production.
- Beef: Provides high-quality protein, zinc, and saturated fat.
- Nuts and Seeds (Almonds, Brazil Nuts, Pumpkin Seeds): Good sources of zinc, magnesium, and healthy fats.
- Pomegranates: Rich in antioxidants that may support testosterone production.
Are Supplements for Testosterone Worth It?
The supplement market is flooded with products claiming to be miraculous supplements for testosterone.
It’s crucial to separate scientific evidence from marketing hype.
The “Must-Haves”: Vitamin D and Zinc
Before considering any exotic herbs, ensure your foundational micronutrient levels are optimal.
The two most important supplements are those that correct common deficiencies:
- Vitamin D: Often called the “sunshine vitamin”, it functions as a steroid hormone in the body. Many people are deficient, and some studies suggest that correcting a Vitamin D deficiency can significantly increase testosterone levels. However, evidence is mixed, and it likely won’t boost levels in those who are already sufficient.
- Zinc: As mentioned, supplementing with zinc is highly effective for individuals who are deficient. If your diet is low in zinc-rich foods, a supplement can be beneficial.
Evidence-Based Herbal Supplements: Ashwagandha and More
A few herbal supplements have promising research behind them:
- Ashwagandha: This adaptogenic herb is best known for its ability to reduce stress and cortisol. By lowering cortisol, it can indirectly support testosterone. Some studies have also shown a direct increase in testosterone in men taking ashwagandha extract.
- Fenugreek: Another herb that has shown potential in several studies to increase both total and free testosterone levels.
- Ginger: While more research is needed in humans, preliminary studies, primarily in animals, suggest ginger may have a positive effect on testosterone production.
The Hype vs. Reality: A Warning About “T-Booster” Blends
Be extremely cautious of proprietary “testosterone booster” blends.
A 2019 study analyzed the top T-booster supplements and found that while 90% claimed to boost testosterone, less than 25% had any data to support their claims.
Many contain under-dosed ingredients or unproven substances.
Stick to single-ingredient supplements with solid research behind them.
| Supplement | Mechanism of Action | Scientific Evidence | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D3 | Functions as a steroid hormone, may improve testicular function. | Moderate (Strong for deficient individuals) | People with low sun exposure or confirmed deficiency. |
| Zinc | Essential cofactor for testosterone synthesis. | Strong (For deficient individuals) | Those with low dietary zinc intake or confirmed deficiency. |
| Ashwagandha | Reduces cortisol (stress hormone), may directly stimulate production. | Promising | Individuals experiencing high stress. |
| Fenugreek | May inhibit enzymes that convert testosterone to estrogen. | Promising | Men looking for libido and strength support. |
Natural Methods vs. Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT)
It’s important to distinguish between natural optimization and medical intervention.
Natural methods aim to help your body produce its own testosterone optimally.
Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) involves administering exogenous (external) testosterone when your body cannot produce enough on its own.
When Are Natural Methods Enough?
Natural methods are the first and best line of defense for most men.
They are ideal for those with levels in the low-normal range or those simply looking to optimize their health.
By addressing the root causes—poor sleep, high stress, bad diet, inactivity—you can often achieve significant improvements in both your testosterone levels and overall well-being without medical intervention.
Understanding the Risks and Benefits of TRT
TRT is a legitimate and life-changing medical treatment for men with clinically diagnosed hypogonadism.
The benefits can include restored libido, increased energy, improved mood, and greater muscle mass. However, it is not without risks.
According to the Mayo Clinic, potential risks include acne, sleep apnea, and an increased red blood cell count.
A major consideration is that TRT shuts down your body’s natural ability to boost testosterone, which can lead to testicular shrinkage and infertility.
It is a lifelong commitment and should only be undertaken under the strict supervision of a qualified medical professional.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How quickly can I naturally increase my testosterone?
Some changes, like those from exercise and sleep, can affect levels acutely within days. However, significant and stable improvements from lifestyle changes like weight loss and diet typically take several weeks to months of consistent effort.
Do testosterone boosters actually work?
Most over-the-counter “T-booster” blends are ineffective and not supported by science. Single-ingredient supplements like Vitamin D, Zinc, and Ashwagandha can work, but primarily if you are deficient or have specific issues like high stress.
Does masturbation or sex affect testosterone levels?
Sexual activity can cause a temporary, short-term spike in testosterone, but it does not have a significant long-term impact on your baseline levels. Abstinence for a week may slightly raise levels, but the effect is minor.
What is a “normal” testosterone level for my age?
Normal ranges vary, but for adult men, it’s generally between 300 to 1,000 ng/dL. Levels naturally decline with age, so what’s normal for a 25-year-old is different from a 65-year-old. A doctor can interpret your results based on your specific age and symptoms.
Can women also benefit from these methods?
Yes. While the focus is often on men, women also need testosterone for health. Lifestyle strategies like quality sleep, stress management, and resistance training are beneficial for hormonal balance in both sexes, though the hormonal outcomes will differ.
Is coffee bad for testosterone?
The research is mixed but generally suggests that moderate coffee consumption is not harmful and may even be beneficial. Some studies show a slight acute increase in testosterone after caffeine intake, especially before exercise.
Will fasting increase or decrease testosterone?
Short-term intermittent fasting may increase luteinizing hormone and potentially testosterone. However, prolonged, severe calorie restriction or long-term fasting can lower testosterone levels as the body goes into a conservation mode.
What are the biggest mistakes people make when trying to boost testosterone?
The biggest mistakes are relying on unproven “booster” pills instead of foundational habits, overtraining without adequate recovery, and adopting extreme low-fat or low-carb diets that deprive the body of essential nutrients for hormone production.
Conclusion
The process to boost testosterone naturally isn’t about finding a single magic pill or workout.
It’s about building a sustainable lifestyle that supports your body’s innate ability to produce this vital hormone.
The four pillars—intelligent exercise, a nutrient-dense diet, restorative sleep, and proactive stress management—work synergistically to create profound improvements not just in your testosterone levels, but in every aspect of your health.
By focusing on these evidence-based strategies, you empower yourself to take control of your vitality.
Start by implementing one or two of these changes today.
Be patient, be consistent, and always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice on your journey to optimal hormonal health.

