Feeling tired, moody, and struggling with stubborn weight gain, no matter what you do?
You might be dealing with a hidden hormonal disruptor: estrogen dominance.
This condition occurs when the delicate balance between estrogen and its counterpart, progesterone, is thrown off, leading to an excess of estrogenic activity in the body.
While hormonal fluctuations are normal, a persistent state of high estrogen can impact everything from your mood and menstrual cycle to your long-term health.
This comprehensive guide will illuminate the complex world of estrogen dominance.
We’ll explore its subtle and overt symptoms, uncover the root causes—from diet to environmental toxins—and provide actionable, evidence-based strategies to help you restore your estrogen progesterone balance and reclaim your vitality.
Get ready to move from confusion to clarity on your journey to better women’s hormonal health.
In This Article
What Exactly Is Estrogen Dominance?
The term “estrogen dominance”, has gained significant traction in wellness circles, but what does it actually mean?
Understanding this concept is the first step toward addressing the symptoms it can cause.
It’s not just about having high estrogen levels, it’s about the relationship between hormones.
Beyond the Hype: A Clear Definition
Estrogen dominance is a state of hormonal imbalance where the level of estrogen is disproportionately high relative to the level of progesterone. This can happen in three primary scenarios:
- Excess Estrogen Production: The body produces too much estrogen.
- Low Progesterone: Estrogen levels might be normal, but progesterone levels are too low to effectively counteract estrogen’s effects. This is common in perimenopause and anovulatory cycles (cycles where ovulation doesn’t occur).
- Improper Estrogen Metabolism: The body struggles to break down and eliminate estrogen efficiently, leading to a buildup of potent estrogen metabolites.
As the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs notes, this imbalance can be due to overproduction, changes in metabolism, or a shift in the estrogen-to-progesterone ratio.
It’s this relative imbalance that drives the symptoms associated with the condition.
The Critical Dance: Understanding the Estrogen-Progesterone Balance
Think of estrogen and progesterone as dance partners.
Estrogen is the “proliferative” hormone—it builds the uterine lining, stimulates breast tissue, and contributes to body fat storage.
Progesterone is the “balancing” hormone—it maintains the uterine lining, promotes calmness, and has a natural diuretic effect.
When they are in sync, your cycle is regular, your mood is stable, and your body functions optimally. When estrogen dominates, it’s like one partner is leading too aggressively, stepping on the other’s toes and disrupting the entire performance. This “unopposed estrogen” can lead to overstimulation of tissues, causing symptoms like heavy periods and tender breasts.
This delicate balance is crucial for overall health.
A 2020 review in the journal Climacteric emphasized that for women’s health, progesterone’s role in balancing estrogen is often ignored, despite its importance for preventing issues like endometrial hyperplasia. .
Is Estrogen Dominance a Formal Medical Diagnosis?
It’s important to note that “estrogen dominance”, is a term more commonly used in functional and integrative medicine than in conventional endocrinology.
While conventional medicine certainly recognizes conditions caused by high estrogen symptoms (like those from PCOS or certain tumors), the concept of a *relative* imbalance is a more nuanced perspective.
However, the symptoms are very real, and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to this imbalance is a valid and effective approach to improving health, regardless of the terminology used.
What Are the Telltale Symptoms of High Estrogen?
The signs of estrogen dominance can be wide-ranging and often overlap with other conditions, making it tricky to pinpoint.
Symptoms can manifest physically, mentally, and emotionally, affecting your quality of life.
Common Symptoms of Estrogen Dominance in Women
When estrogen levels are high relative to progesterone, women may experience a cluster of characteristic symptoms.
According to sources like Cleveland Clinic and Medical News Today, these include:
- Weight Gain: Particularly stubborn fat around the hips, waist, and thighs.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Heavy, painful periods (menorrhagia), or shorter cycles.
- Worsened PMS: Increased breast tenderness, bloating, headaches, and mood swings before your period.
- Mood Swings, Anxiety, and Irritability: Estrogen influences neurotransmitters like serotonin, and an imbalance can disrupt mood regulation.
- Fatigue and Sleep Disturbances: Feeling exhausted despite getting enough sleep, or having trouble falling/staying asleep.
- Low Libido: An imbalance can suppress sexual desire.
- Fibrocystic Breasts: Lumpy, tender breast tissue.
- Uterine Fibroids: Non-cancerous growths in the uterus that are fueled by estrogen.
- Hair Loss: Thinning hair on the scalp.
- Brain Fog: Difficulty concentrating and memory issues.
How Excess Estrogen Affects Men
Men also produce estrogen, albeit in smaller amounts, and require a healthy balance with testosterone.
When men experience excess estrogen, it can lead to:
- Gynecomastia: The development of enlarged breast tissue.
- Erectile Dysfunction (ED): Difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection.
- Infertility: Estrogen plays a role in sperm production, and high levels can impair it.
- Fatigue and Emotional Disturbances: Similar to women, men can experience mood changes and low energy.
A Deeper Look: Connecting Symptoms to the Imbalance
Why does excess estrogen cause these specific issues? It comes down to its primary functions.
Estrogen’s role is to stimulate growth.
When unopposed by progesterone, this stimulation can go into overdrive:
- It promotes the growth of the uterine lining, leading to heavy periods.
- It stimulates breast tissue, causing tenderness and fibrocystic changes.
- It encourages fat cells to store more fat, contributing to weight gain.
- It can increase water and salt retention, leading to bloating.
Understanding these connections helps demystify why you’re feeling the way you do and reinforces that these symptoms are not “just in your head”.
What Causes the Body to Have Excess Estrogen?
Estrogen dominance is rarely caused by a single factor.
It’s typically the result of a combination of internal processes, lifestyle habits, and environmental exposures that disrupt the body’s natural hormonal harmony.
Internal Factors: Your Body’s Own Production
- Obesity: Fat tissue (adipose tissue) is not just for storage, it’s an endocrine organ that produces and stores estrogen. Research shows that higher body fat is directly linked to higher circulating estrogen levels.
- Chronic Stress: When you’re under constant stress, your body pumps out cortisol. The production of cortisol uses progesterone as a precursor, a phenomenon sometimes called “progesterone steal”. This can lower progesterone levels, leaving estrogen unopposed.
- Hormonal Conditions: Conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) are often associated with hormonal imbalances, including potential estrogen dominance due to irregular ovulation and lower progesterone.
The Liver’s Role: Inefficient Estrogen Detox
Your liver is the primary organ responsible for breaking down hormones, including estrogen.
This process, known as estrogen detox, occurs in two phases:
- Phase I: Enzymes convert potent estrogens into weaker, more water-soluble forms. This phase can sometimes create more harmful metabolites if not properly balanced.
- Phase II: The liver attaches compounds (like glucuronic acid or sulfate) to these metabolites, neutralizing them and preparing them for excretion.
If the liver is overburdened—due to a poor diet, high alcohol intake, or nutrient deficiencies (like B vitamins and magnesium)—it cannot perform this detoxification process efficiently.
This leads to a recirculation of potent estrogens in the bloodstream.
A review from the Metagenics Institute highlights the importance of balancing these two liver phases for healthy estrogen clearance.
Gut Health: The Missing Link in Estrogen Excretion
After the liver processes estrogen, it’s sent to the gut for final elimination.
The health of your gut microbiome plays a surprisingly critical role here.
A specific collection of gut bacteria, known as the estrobolome, produces an enzyme called beta-glucuronidase.
If this enzyme is overactive (often due to gut dysbiosis), it can “un-package” the detoxified estrogen, allowing it to be reabsorbed back into circulation, further contributing to estrogen dominance.
External Factors: Environmental Xenoestrogens
Xenoestrogens are man-made chemicals that mimic the effects of estrogen in the body.
They bind to estrogen receptors and contribute to the overall estrogenic load. Common sources include:
- Plastics: Bisphenol A (BPA) and phthalates found in food containers, water bottles, and can linings.
- Personal Care Products: Parabens and phthalates in lotions, shampoos, and cosmetics.
- Pesticides: Certain pesticides used in conventional agriculture have estrogenic properties.
Lifestyle Triggers: Diet, Alcohol, and Inactivity
- Poor Diet: A diet low in fiber and high in processed foods and refined sugars can impair gut health and liver function, hindering estrogen excretion.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol places a direct burden on the liver, prioritizing its own metabolism over hormone detoxification. It can also increase the conversion of testosterone to estrogen.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and supports detoxification pathways.
How Can You Test for and Diagnose Estrogen Dominance?
If you suspect you have estrogen dominance, getting tested can provide valuable data to confirm the imbalance and guide your treatment strategy.
However, testing for hormonal balance is more complex than a single blood draw.
Blood, Saliva, or Urine? Understanding Your Testing Options
There are several methods to assess hormone levels, each with its pros and cons:
- Blood (Serum) Testing: This is the most common method used in conventional medicine. It measures the total amount of hormones circulating in your blood. It’s excellent for getting a snapshot of levels but may not reflect the “free” or bioavailable hormones that your tissues are actually using.
- Saliva Testing: This method measures the free, unbound hormones that have passed from the bloodstream into saliva. Proponents argue it better reflects the hormones actively available to tissues. It’s often used in functional medicine to assess cortisol and sex hormone rhythms.
- Urine Testing (e.g., DUTCH Test): Dried Urine Testing for Comprehensive Hormones (DUTCH) is a popular, advanced option. It not only measures hormone levels but also their metabolites. This provides crucial insight into *how* your body is breaking down and detoxifying estrogen, which is key for understanding estrogen dominance.
Interpreting Your Results: It’s About Ratios, Not Just Numbers
A crucial part of diagnosing estrogen dominance is looking beyond individual hormone levels and analyzing the estrogen progesterone balance.
A practitioner will often calculate the progesterone-to-estradiol ratio.
Even if both hormones are within the “normal” lab range, a low ratio can indicate a relative excess of estrogen and explain your symptoms.
For premenopausal women, timing is also critical, tests should ideally be done during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle (days 19-22 of a 28-day cycle), when progesterone should be at its peak.
When to See a Doctor or Functional Medicine Practitioner
While lifestyle changes can be powerful, it’s essential to work with a qualified healthcare professional. They can:
- Rule out other medical conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
- Order and correctly interpret the right hormone tests for you.
- Create a personalized treatment plan that may include diet, supplements, and, if necessary, bioidentical hormone therapy.
- Monitor your progress and adjust your plan as needed.
How to Reduce Estrogen: A Strategic Approach to Hormonal Balance
Restoring your estrogen progesterone balance requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses diet, detoxification, and lifestyle.
Here are four key strategies to help you naturally reduce your estrogen load.
Strategy 1: The Estrogen Detox Diet
What you eat has a profound impact on your hormones.
The goal is to consume foods that support liver detoxification and promote the healthy excretion of estrogen.
- Load Up on Cruciferous Vegetables: Broccoli, cauliflower, kale, cabbage, and Brussels sprouts are rich in a compound called Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C), which converts to Diindolylmethane (DIM) in the gut. These compounds help steer estrogen metabolism toward healthier, less potent pathways.
- Prioritize Fiber: Aim for 35-40 grams of fiber per day from sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, psyllium husk, legumes, and whole grains. Fiber binds to excess estrogen in the gut and ensures it’s eliminated rather than reabsorbed. A study published in the National Library of Medicine found that high-fiber diets promote healthier estrogen levels.
- Include Phytoestrogens: Foods like ground flaxseeds and organic, non-GMO soy (in moderation) contain weak plant-based estrogens. These can bind to estrogen receptors, blocking more potent endogenous estrogens and xenoestrogens from binding.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids found in wild-caught fish, walnuts, and chia seeds have anti-inflammatory properties that support overall hormonal health.
| Foods to Embrace | Foods to Limit or Avoid |
|---|---|
| Cruciferous Vegetables (Broccoli, Kale, Cabbage) | Conventionally Raised Meat & Dairy (potential added hormones) |
| High-Fiber Foods (Flaxseeds, Legumes, Oats) | Processed & Refined Sugars (disrupt gut health) |
| Berries and Dark Leafy Greens (Antioxidants) | Excessive Alcohol (burdens the liver) |
| Organic, Non-GMO Soy (Tofu, Tempeh) | Highly Processed Foods with Additives |
| Healthy Fats (Avocado, Olive Oil, Nuts, Seeds) | Plastic-Packaged Foods (potential BPA/phthalates) |
Strategy 2: Supporting Your Liver and Gut Health
A healthy liver and gut are non-negotiable for proper estrogen detox.
You can support these systems through targeted nutrition and lifestyle choices.
- Liver Support: Ensure you’re getting enough B vitamins (especially folate, B6, B12), magnesium, and selenium. Foods like leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and high-quality protein are excellent sources. Herbs like milk thistle and turmeric can also support liver function.
- Gut Health: Incorporate probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut to foster a healthy microbiome. A prebiotic fiber supplement can feed these beneficial bacteria. A healthy gut helps ensure the estrobolome functions correctly to excrete estrogen.
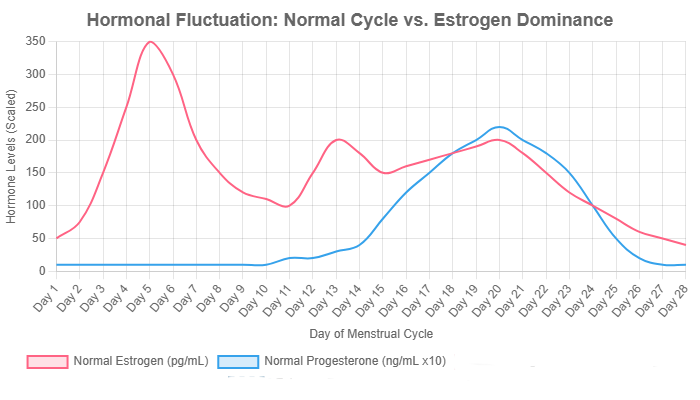
Chart: A visual representation of a normal menstrual cycle versus a state of estrogen dominance, where estrogen remains high and progesterone is suppressed, disrupting the crucial hormonal ratio.
Strategy 3: Lifestyle Modifications for Lasting Change
- Manage Stress: Implement stress-reduction techniques like meditation, deep breathing, yoga, or spending time in nature. This helps lower cortisol and spares your progesterone.
- Prioritize Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Sleep is when your body repairs itself and regulates hormone production.
- Move Your Body: Engage in regular, moderate exercise. Both strength training and cardiovascular exercise help maintain a healthy body composition, improve insulin sensitivity, and support detoxification through sweat.
Strategy 4: Reducing Your Exposure to Xenoestrogens
Minimizing your contact with hormone-disrupting chemicals can significantly lower your body’s overall estrogenic burden.
- Filter Your Water: Use a high-quality water filter to remove chlorine and other potential contaminants.
- Choose Glass Over Plastic: Store food and drink water from glass, stainless steel, or BPA-free containers. Never microwave food in plastic.
- Clean Up Your Personal Care Routine: Opt for natural, fragrance-free lotions, cosmetics, and cleaning products. Check labels for parabens, phthalates, and sulfates.
- Eat Organic When Possible: Prioritize organic versions of produce on the “Dirty Dozen” list to reduce pesticide exposure.
What Are the Long-Term Risks of Unchecked Estrogen Dominance?
While the immediate symptoms of estrogen dominance can be disruptive, the long-term health implications of chronically high estrogen are a more serious concern.
Unopposed estrogen’s proliferative nature can increase the risk of several health conditions.
According to research cited by institutions like the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), prolonged exposure to high estrogen levels is associated with an increased risk of:
- Hormone-Sensitive Cancers: The continuous stimulation of cell growth can increase the risk of breast, uterine, and ovarian cancers. Progesterone helps balance this by signaling cells to mature and stop dividing.
- Endometriosis and Uterine Fibroids: These conditions are fueled by estrogen and can worsen with a persistent imbalance.
- Thyroid Dysfunction: High estrogen can increase levels of thyroid-binding globulin (TBG), which binds to thyroid hormones and reduces the amount of free, usable thyroid hormone in the body, potentially leading to hypothyroid symptoms.
- Blood Clots and Stroke: Estrogen can affect blood clotting factors, and high levels may increase the risk of thromboembolic events.
- Autoimmune Conditions: Some research suggests that estrogen can modulate the immune system, and an imbalance may contribute to the development or flare-ups of autoimmune diseases.
Addressing estrogen dominance is not just about feeling better today, it’s a critical strategy for protecting your long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Estrogen Dominance
1. What is the fastest way to lower estrogen?
There’s no “fast” fix, but a focused approach on a high-fiber, cruciferous-rich diet, limiting alcohol, and supporting liver health can begin to lower estrogen levels. Consistency is more important than speed for lasting hormonal balance.
2. Can estrogen dominance cause weight gain?
Yes, it’s a primary symptom. Excess estrogen promotes fat storage, particularly around the hips and thighs, and can increase water retention, leading to bloating and a higher number on the scale.
3. Does coffee make estrogen dominance worse?
It can. High caffeine intake can burden the liver, which is responsible for estrogen detox. Some studies also show it can alter estrogen levels. Moderation is key, consider switching to green tea, which supports liver health.
4. How does stress affect estrogen levels?
Chronic stress increases cortisol. The production of cortisol can deplete progesterone levels (the “progesterone steal”), leading to a relative excess of estrogen and worsening symptoms of estrogen dominance.
5. What is the difference between high estrogen and estrogen dominance?
High estrogen means your absolute estrogen level is above the normal range. Estrogen dominance is a relative term, your estrogen could be normal, but if your progesterone is too low, you still have a dominant estrogenic effect.
6. Can men have estrogen dominance?
Yes. Men can experience a similar imbalance where their estrogen levels are too high relative to their testosterone. This can be caused by obesity, alcohol, and poor liver function, leading to symptoms like gynecomastia.
7. Are supplements like DIM effective?
Supplements like DIM (Diindolylmethane) can be very effective for supporting healthy estrogen metabolism. However, it’s crucial to work with a healthcare provider to determine the right supplement and dosage for your specific needs.
8. How long does it take to correct estrogen dominance?
It varies, but with consistent diet and lifestyle changes, many people start to notice improvements in symptoms within 1-3 months. Fully rebalancing your hormones can take six months or longer.
Conclusion
Estrogen dominance is more than just a buzzword, it’s a real and impactful hormonal imbalance that affects millions.
Its symptoms—from debilitating fatigue and mood swings to stubborn weight gain and heavy periods—can significantly diminish your quality of life.
The key takeaway is that this condition is about a *relative* imbalance, where the proliferative effects of estrogen are not adequately balanced by the calming influence of progesterone.
The path to restoring your estrogen progesterone balance is rooted in a holistic approach.
By adopting a nutrient-dense diet rich in fiber and cruciferous vegetables, supporting your liver and gut detoxification pathways, managing stress, and reducing your exposure to environmental toxins, you can effectively lower your estrogen load and empower your body to find its natural equilibrium.
If you recognize yourself in the symptoms described, don’t dismiss them as an inevitable part of life.
Take this knowledge as a call to action.
Consult with a trusted healthcare professional, explore testing options, and begin implementing these powerful strategies.
Reclaiming your hormonal health is within your reach.
References
[1] Estrogen Dominance – Whole Health Library – VA.gov
https://www.va.gov/WHOLEHEALTHLIBRARY/tools/estrogen-dominance.asp
[2] High vs. Low Estrogen: Symptoms, Effects, and Management
https://www.draliabadi.com/womens-health-blog/symptoms-of-high-or-low-estrogen
[3] Estrogen Dominance Symptoms, Causes, and Strategies for Hormonal Balance
[4] Let’s Talk About Estrogen Dominance!
https://www.rebellehealth.com/resources/lets-talk-about-estrogen-dominance
[5] Estrogen: The necessary evil for human health, and ways to tame it
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29573619
[6] Hormonal Imbalance: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22673-hormonal-imbalance
[7] Estrogen Dominance in PCOS – TārāMD
https://www.taramd.com/post/estrogen-dominance-in-pcos
[8] Women’s reproductive system as balanced estradiol and …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S174067572030013X
[9] The Myth of Estrogen Dominance – Winona
[10] Estrogen Dominance: Causes, Symptoms, Testing, and Treatments
[11] The effect of estrogen hormone on premenstrual syndrome (PMS …
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0213911121003101
[12] Balancing Estrogen and Progesterone | GYN in Forest Hills, NY
https://women4womenobgyn.com/balancing-estrogen-and-progesterone
[13] High Estrogen: Causes, Symptoms, Dominance & Treatment
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22363-high-estrogen
[14] 7 signs of a hormonal imbalance — and what to do about it
https://www.uclahealth.org/news/article/7-signs-hormonal-imbalance-and-what-do-about-it
[15] [PDF] Estrogen metabolism | Metagenics Institute
[16] How to Support Estrogen Detoxification Naturally
https://stramcenter.com/blog/blog-detail/how-to-support-estrogen-detoxification-naturally
[17] The basics of estrogen detoxification – FUTURE WOMAN
https://future-woman.com/the-basics-of-oestrogen-detox/
[18] How Your Diet Can Affect Estrogen Levels – Healthline
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods-to-lower-estrogen
[19] Estrogen Dominance
https://www.amcenters.com/en/kyiv/blog/estrogen-dominance
[20] Treat High Estrogen Dominance Naturally: Food Diet & Lifestyle

