In the vast world of herbal medicine, few topics have garnered as much recent attention as the potential ashwagandha benefits.
This ancient herb, a cornerstone of Ayurvedic tradition for millennia, is now a global phenomenon, celebrated for its potential to combat modern-day ailments like stress and fatigue.
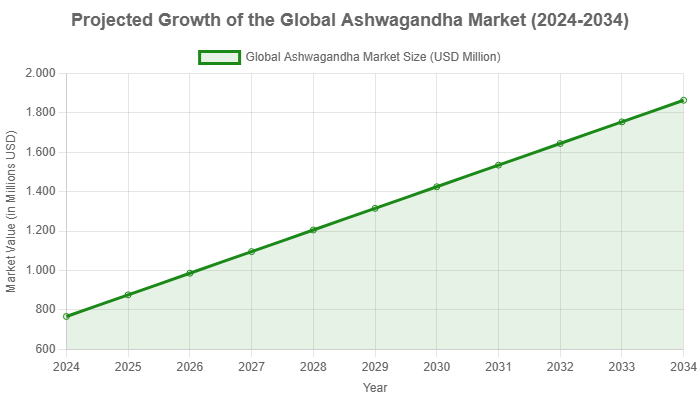
The global ashwagandha market was valued at approximately $766 million in 2024 and is projected to soar to over $1.8 billion by 2034, a testament to its surging popularity (Precedence Research).
But what exactly is behind this explosive growth?
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the science of Ashwagandha, exploring its evidence-backed benefits, recommended dosages for various goals, and the crucial safety information you need to know before incorporating it into your wellness routine.
In This Article
What is Ashwagandha?
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is a small evergreen shrub with yellow flowers, native to India, the Middle East, and parts of Africa.
Its name in Sanskrit translates to “smell of the horse”, referring to both its unique root aroma and the traditional belief that it imparts the strength and vitality of a stallion.
While it’s sometimes called “Indian ginseng”, it is not botanically related to the ginseng family.
For over 3,000 years, it has been a revered herb in Ayurveda, the traditional system of medicine in India, used as a *Rasayana*—a tonic for rejuvenation, longevity, and overall vitality.
Today, modern science is beginning to validate many of these traditional uses, especially the ashwagandha benefits related to its role as an adaptogen.
Understanding Adaptogens and Withanolides
Ashwagandha is classified as an adaptogen.
Adaptogens are a unique class of herbs and mushrooms that help the body resist and adapt to physical, chemical, and biological stressors.
Instead of having a specific action, they work to normalize body functions and strengthen the systems compromised by stress.
As Myles Spar, M.D., explained to Forbes Health, adaptogens “help calm the nervous system without making people feel tired”.
The primary active compounds responsible for the ashwagandha benefits are a group of steroidal lactones called withanolides.
These phytochemicals are believed to modulate the body’s stress pathways, particularly the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is our central stress response system.
By helping to regulate cortisol, the body’s primary stress hormone, withanolides can mitigate the physiological impact of chronic stress.
KSM-66 vs. Other Extracts: What’s the Difference?
When shopping for Ashwagandha, you’ll often encounter branded extracts like KSM-66, Sensoril, and Shoden.
These are not just different brands; they represent different extraction methods and concentrations.
- KSM-66: This is a highly concentrated, full-spectrum root-only extract. It is standardized to contain a high percentage (typically 5%) of withanolides and is one of the most extensively researched forms of Ashwagandha in clinical trials. It’s often favored for its balanced effects on stress, cognition, and athletic performance.
- Sensoril: This extract is derived from both the roots and leaves of the plant. It is standardized to a higher concentration of withanolide glycosides (around 10%). Due to its composition, it is often perceived as having more calming or sedating effects, making it popular for sleep and anxiety support.
- Shoden: A newer, highly bioavailable extract standardized to an impressive 35% withanolide glycosides. Its high potency means smaller doses may be effective.
The choice between them often depends on the desired outcome, as different extracts may be better suited for specific ashwagandha benefits.
However, KSM-66 is frequently cited in studies focusing on a broad range of effects.
Ashwagandha Benefits: A Guide to the Science-Backed Health Effects
While traditional use provides a rich history, modern clinical research is crucial for validation.
Here are some of the most well-supported benefits of Ashwagandha.
1. Reducing Stress and Anxiety
This is one of the most celebrated ashwagandha benefits.
Multiple studies have demonstrated its efficacy in reducing perceived stress and anxiety.
A 2021 systematic review published in the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Fact Sheet analyzed seven studies and found that Ashwagandha significantly reduced stress levels, sleeplessness, fatigue, and serum cortisol compared to a placebo.
The benefits appeared greater with daily doses of 500-600 mg.
A landmark study published in the Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine found that participants taking 300 mg of high-concentration, full-spectrum Ashwagandha root extract (KSM-66) twice daily for 60 days had a 27.9% reduction in serum cortisol levels and significant improvements on stress-assessment scales. (Source: PubMed Central)
2. Improving Sleep Quality
Given its calming effects, Ashwagandha’s ability to improve sleep is a logical extension.
Research suggests it helps people fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and experience better sleep quality.
A 2021 meta-analysis of five clinical trials concluded that Ashwagandha extract had a small but significant positive effect on overall sleep.
The benefits were most pronounced in individuals with insomnia and those taking 600 mg daily for at least 8 weeks (Source: PubMed).
3. Enhancing Cognitive Function
Another one of the key ashwagandha benefits is its positive impact on brain health, including memory, attention, and information-processing speed.
The antioxidant properties of its compounds, including withaferin A, are thought to protect the brain from oxidative stress.
A 2024 study found that 225 mg of Ashwagandha over 30 days improved word recall and mental reaction time (as cited by Forbes).
Another study in 2024 published in PubMed showed that Ashwagandha root extract improved cognition, energy, and mood in participants (Source: PubMed).
4. Boosting Athletic Performance and Muscle Strength
Ashwagandha may be a valuable supplement for athletes and active individuals.
Research indicates it can improve physical performance by increasing strength and oxygen use during exercise.
A key metric, VO₂ max—the maximum amount of oxygen a person can utilize during intense activity—has been shown to improve with Ashwagandha supplementation.
A 2024 study on the effects of 600 mg of standardized root extract found significant improvements in muscle size, strength, and recovery in resistance-trained individuals, highlighting significant ashwagandha benefits for fitness enthusiasts (Source: PubMed).
5. Supporting Hormonal Health
Ashwagandha has shown promise in balancing hormones, benefiting both men and women.
- For Men: Several studies have linked Ashwagandha to increased testosterone levels. A 2019 study found that overweight men aged 40-70 who took an ashwagandha extract for eight weeks had a 14.7% greater increase in testosterone compared to the placebo group (as cited by Healthline). It may also improve sperm concentration and motility.
- For Women: Research suggests Ashwagandha can improve sexual function in women. A 2022 study found that women taking 600 mg of Ashwagandha daily experienced significant improvements in arousal, lubrication, orgasm, and overall satisfaction.
6. Anti-Inflammatory and Immune Support
Chronic inflammation is linked to numerous health problems.
Ashwagandha contains compounds, particularly withaferin A, that have been shown to reduce markers of inflammation, such as C-reactive protein (CRP).
By modulating inflammatory pathways and enhancing the activity of immune cells like natural killer cells, Ashwagandha may help support a healthy immune response.
The Meteoric Rise of Ashwagandha
The growing body of scientific evidence for ashwagandha benefits, coupled with a global shift towards natural wellness solutions, has fueled the herb’s incredible market growth.
Consumers are increasingly seeking out adaptogens to manage the pressures of modern life, and Ashwagandha has emerged as a leader in this category.
The chart below illustrates the projected growth of the global Ashwagandha market, reflecting its transition from a traditional remedy to a mainstream supplement.
Dosage and How to Use Ashwagandha Effectively
Determining the right dosage depends on the form of Ashwagandha and your health goals.
There is no single “correct” dose, but clinical studies provide a reliable range.
General Dosage Guidelines
Most research has used doses ranging from 250 mg to 600 mg per day of a standardized extract, often split into two doses (e.g., one in the morning and one in the evening).
For general stress relief, a common starting point is 300 mg once or twice daily.
The ideal dosage often depends on the specific ashwagandha benefits you are seeking.
- For Stress and Anxiety: Studies show efficacy in the 500-600 mg/day range.
- For Sleep: Doses of 600 mg/day for at least 8 weeks have shown the most prominent results for those with insomnia.
- For Athletic Performance: Doses around 600 mg/day are commonly used in studies showing benefits in strength and VO₂ max.
It’s generally recommended to take Ashwagandha for at least 30 days to notice its effects, as adaptogens work by gradually helping the body build resilience over time.
Dosage Comparison for Different Goals
This table provides a summary of typical dosages used in research for various benefits.
Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement.
| Health Goal | Typical Daily Dosage (Standardized Extract) | Common Form Used in Research | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Stress Reduction | 300 – 600 mg | KSM-66 Root Extract | Can be taken as a single dose or split into two. |
| Anxiety Management | 500 – 600 mg | KSM-66 or Sensoril | Higher end of the range often used in clinical trials. |
| Improved Sleep Quality | 600 mg | KSM-66 or Sensoril | Often taken in the evening. Effects are more pronounced with consistent use over 8+ weeks. |
| Cognitive Enhancement | 225 – 600 mg | KSM-66 or NooGandha | Benefits memory, focus, and processing speed. |
| Athletic Performance | 600 – 1,000 mg | KSM-66 Root Extract | Improves VO₂ max, strength, and muscle recovery. |
| Testosterone Support (Men) | 300 – 600 mg | KSM-66 Root Extract | Studies show modest but significant increases. |
Safety, Side Effects, and Important Precautions
Ashwagandha is considered safe for most people for short-term use (up to 3 months). However, it’s not without potential side effects and contraindications.
The long-term safety beyond this period is not well-established.
Common and Rare Side Effects
Most side effects are mild and gastrointestinal in nature.
These can include:
- Stomach upset or discomfort
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
- Drowsiness or sedation
More serious, though rare, side effects have been reported.
While the ashwagandha benefits are appealing, it’s crucial to be aware of potential risks.
The NIH’s LiverTox database notes several case reports linking high doses or contaminated Ashwagandha supplements to liver injury.
Symptoms resolved after discontinuing the supplement.
There are also rare case reports of thyrotoxicosis (excess thyroid hormone) in individuals taking Ashwagandha, suggesting it may stimulate thyroid function.
Who Should Avoid Ashwagandha?
Certain populations should exercise caution or avoid Ashwagandha altogether:
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: Ashwagandha is considered likely unsafe during pregnancy, as it may have abortifacient properties. Its safety during breastfeeding is unknown.
- People with Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, or multiple sclerosis should avoid Ashwagandha, as it may stimulate the immune system and worsen symptoms.
- People with Thyroid Disorders: Since it can increase thyroid hormone levels, those with hyperthyroidism or on thyroid medication should consult a doctor.
- Individuals with Hormone-Sensitive Prostate Cancer: Because it may increase testosterone levels, it is not recommended for this group.
- Those Undergoing Surgery: Ashwagandha may slow the central nervous system. It’s advised to stop taking it at least two weeks before scheduled surgery.
Potential Drug Interactions
Ashwagandha can interact with several types of medications.
According to the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, you should be cautious if you take:
- Sedatives (Benzodiazepines, Barbiturates): Ashwagandha can have a sedative effect, which may be amplified when combined with these drugs.
- Immunosuppressants: Its immune-stimulating properties may counteract the effects of these medications.
- Thyroid Hormone Medication: It may increase thyroid hormone levels, potentially interfering with medication dosage.
- Antidiabetes and Antihypertensive Drugs: It may lower blood sugar and blood pressure, potentially enhancing the effects of these drugs and requiring a dosage adjustment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does it take for Ashwagandha to work?
Effects are not immediate. Most studies show noticeable ashwagandha benefits after 4 to 12 weeks of consistent daily use as the body adapts.
2. Can I take Ashwagandha every day?
Daily use for up to 3 months is considered safe for most people. The long-term effects of continuous daily use are not well-studied, so some experts recommend cycling it (e.g., 3 months on, 1 month off).
3. What’s the main difference between KSM-66 and regular Ashwagandha?
KSM-66 is a patented, full-spectrum root extract with a standardized 5% concentration of withanolides. “Regular” Ashwagandha can be a simple root powder or a non-standardized extract, with variable potency and quality.
4. Does Ashwagandha actually increase testosterone?
Yes, multiple clinical studies have shown that Ashwagandha supplementation can lead to a modest but statistically significant increase in testosterone levels in men, particularly those who are stressed or have low levels.
5. Will Ashwagandha make me feel tired or drowsy?
It can. While it’s an adaptogen that helps balance energy, its calming effect on the nervous system can cause drowsiness in some individuals, especially at higher doses or when first starting.
6. Is Ashwagandha safe for long-term use?
The safety of use beyond 3 months has not been rigorously studied in clinical trials. It is best to consult a healthcare provider for guidance on long-term supplementation.
7. Why is Ashwagandha banned in some countries like Denmark?
Some regulatory bodies, like the one in Denmark, have raised concerns about its potential effects on thyroid and sex hormones and a historical (though debated) association with causing miscarriages, leading them to ban its use as a precaution.
8. Can Ashwagandha help with weight loss?
Indirectly, perhaps. By reducing the stress hormone cortisol, which is linked to abdominal fat storage and stress-induced cravings, Ashwagandha may help support weight management efforts, but it is not a direct weight loss supplement.
Conclusion
Ashwagandha has rightfully earned its place as a premier adaptogen in the modern wellness toolkit.
The scientific evidence supporting the ashwagandha benefits for stress reduction, sleep improvement, cognitive function, and physical performance is compelling and continues to grow.
Its ability to modulate the body’s stress response system offers a powerful, natural approach to building resilience in a high-pressure world.
However, its power demands respect.
Ashwagandha is not a one-size-fits-all remedy and is not appropriate for everyone.
Understanding the correct dosage, potential side effects, and crucial contraindications is paramount.
The quality and form of the extract—such as the well-researched KSM-66—also play a significant role in its efficacy and safety.
Ultimately, while Ashwagandha can be a valuable ally for health, it should be part of a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest.
Before adding Ashwagandha or any supplement to your regimen, the most important step is to consult with a qualified healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your individual health needs.

